Have you ever wondered how companies consistently create products that meet the needs of customers? The answer lies in a powerful methodology known as Quality Function Deployment (QFD). QFD is a method for developing customer-oriented products (Ginting et al., 2020).
QFD is a systematic approach that translates customer requirements into product and service characteristics. It ensures that products and services are designed to meet the needs and expectations of customers, resulting in increased customer satisfaction, improved quality, and cost reduction.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Quality Function Deployment implementation, exploring its origins, benefits, key features, and practical applications. We will also provide valuable resources to help you implement Quality Function Deployment (QFD) in your organization.
What is Quality Function Deployment (QFD)?
QFD was developed in Japan in the 1960s by Yoji Akao, and introduced to Europe and America in 1983 (Jaiswal, 2012). It was first used in the automotive industry but has since been adopted in a wide range of industries, such as electronics, aerospace, and medical.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD), also known as “Despliegue de la Función de Calidad” in Spanish, is defined as a methodology for transforming customer needs and expectations into product and service characteristics. It is based on the idea that the quality of a product or service is directly related to customer satisfaction.
Additionally, Ginting et al., (2020) highlight that QFD is a planning process that helps the organization plan the implementation of various technical support tools effectively and complement each other to prioritize each problem.
In summary, Quality Function Deployment is a quality tool that helps turn the “voice of the customer” into new products that meet their needs (Jaiswal, 2012). Quality Function Deployment acts as a bridge between customer desires and product design, ensuring an optimized process that enhances overall quality.
The Basic Principles of Quality Function Deployment
Essentially, QFD is guided by several key principles:
- Customer Focus: Placing the customer at the center of the product development process ensures that companies meet real-world needs and preferences.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Quality Function Deployment fosters collaboration between departments, promoting communication and alignment throughout the organization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By relying on data and metrics, companies can make informed decisions that drive product excellence and innovation.
- Continuous Improvement: QFD is not a one-time event but rather a continuous journey of refinement and optimization. By adopting a mindset of continuous improvement, companies can stay ahead and remain competitive in their respective industries.
Benefits of QFD
A central element of QFD is the prioritization of customer requirements. Understanding the voice of the customer is crucial to identifying key features and functionalities that generate satisfaction. Through rigorous data analysis and customer feedback, companies can discern the most critical aspects of their products, guiding the development process effectively. From this, QFD offers a range of benefits for companies, including:
- Improved Quality: QFD ensures that products and services are designed with customer needs in mind, improving quality, reducing defects, and enhancing overall quality.
- Reduced Costs: By identifying and eliminating unnecessary functions and processes, Quality Function Deployment helps organizations reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Increased Market Share: By offering products and services that meet customer needs, QFD helps organizations attract new customers and increase market share. Erdil and Arani (2019) report significant improvements in critical quality characteristics identified and sales rates as a result of using QFD.
- Improved Communication: Quality Function Deployment promotes communication and collaboration between different departments within an organization, fostering a culture of teamwork and continuous improvement.
Beyond its role in product development, QFD catalyzes innovation. By fostering a culture of creativity, adaptation, and problem-solving, companies can explore new avenues of growth and differentiation. Quality Function Deployment encourages experimentation and risk-taking, allowing organizations to stay ahead in dynamic market environments.
Applications of Quality Function Deployment
Quality Function Deployment can be applied in a wide range of industries and environments, including:
- Product Development: QFD is widely used in the development of new products and services to ensure they meet customer needs and expectations.
- Process Improvement: Quality Function Deployment can be used to improve existing processes by identifying and eliminating waste and inefficiencies.
- Service Design: QFD can be used to design and improve services to ensure they meet customer expectations and provide a high level of satisfaction.
- Project Management: Quality Function Deployment can be used in project management to ensure that projects are aligned with customer needs and priorities.
Tools and Techniques for QFD
In addition to the QFD Matrix, several tools and techniques complement the QFD methodology. From benchmarking and competitive analysis to performance metrics and stakeholder engagement, these tools provide valuable insights and support throughout the product development lifecycle. However, the most commonly used are:
- House of Quality: The House of Quality is a matrix used to relate customer requirements to technical requirements.
- Affinity Diagrams: Affinity diagrams are used to organize and group related ideas and concepts.
- Tree Diagrams: Tree diagrams are used to break down complex concepts into smaller, manageable components.
- Interrelationship Digraphs: Interrelationship digraphs are used to identify and analyze relationships between different elements.
What is the House of Quality (HOQ)?
At the heart of QFD lies the House of Quality, a fundamental framework that visually represents the relationships between customer requirements and design characteristics. Through the House of Quality, companies gain clarity and insight into the interconnection of various factors, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Ginting et al., (2020) report that the House of Quality (HOQ) is a QFD tool used to determine design boundaries, show the relationship between survey respondents’ needs and the matrix to meet respondents’ needs, and illustrate the design team’s approach to producing quality products.
The House of Quality (HOQ) is a matrix used to relate customer needs to product and service characteristics.
How to Build a House of Quality
To build a House of Quality, the following steps are followed:
- Identify customer needs: The first step is to identify customer needs. This can be done through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and other market research techniques. However, as warned by Klochkov et al., (2016) we should not overlook the fact that this approach is based on the analysis of consumer opinions, so when using QFD, specific aspects of human perception should be taken into account; in the same vein, Xiao and Wang (2024) integrated a consensus-seeking process based on optimization into QFD to deal with conflicting customer opinions, where customer opinions are modeled with incomplete linguistic distribution assessments.
- Identify product or service characteristics: The next step is to identify product or service characteristics. These are the features that will satisfy customer needs. In this regard, Zare (2010) emphasizes that for product development tasks to be successful and provide competitive advantages, management must commit to customer needs and implement them in the product development process by converting them into engineering design requirements.
- Relate customer needs to product or service characteristics: The next step is to relate customer needs to product or service characteristics. This is done in the House of Quality matrix.
- Prioritize customer needs: The next step is to prioritize customer needs. This can be done using a series of criteria, such as the importance of the need to the customer and the difficulty of satisfying it.
- Develop an action plan: The final step is to develop an action plan to meet customer needs. This plan should include the necessary resources, schedule, and responsibilities.
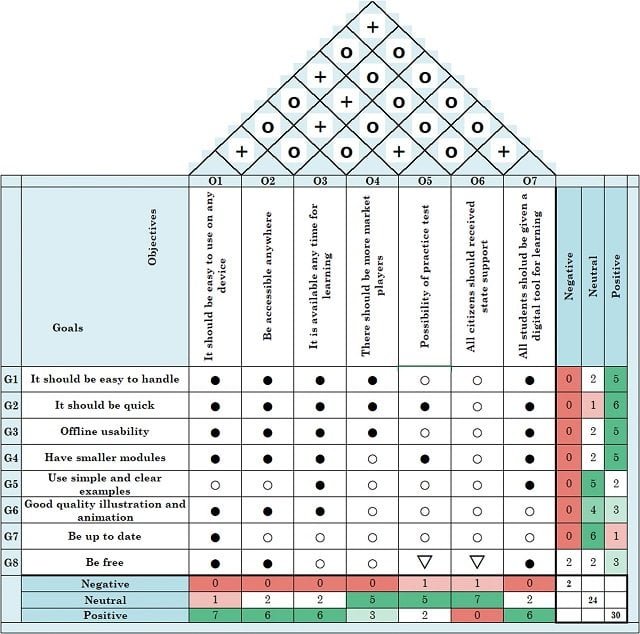
Uses of the House of Quality
The House of Quality can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Development of new products or services: The House of Quality can be used to help companies develop new products or services that meet customer needs.
- Improvement of existing products or services: The House of Quality can be used to help companies improve existing products or services.
- Strategic planning: The House of Quality can be used to help companies develop strategic plans that focus on customer needs.
How to Implement QFD
The following are the steps involved in implementing QFD:
- Define the project: The first step is to define the project, including the scope, objectives, and team.
- Identify customer requirements: The next step is to identify customer requirements. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Prioritize customer requirements: Once customer requirements have been identified, it is necessary to prioritize them. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as the Kano model.
- Develop the House of Quality: The next step is to develop the House of Quality. This involves relating customer requirements to product or service characteristics. In the study by Buics et al., (2024), you can find an example of the application of the House of Quality regarding the traffic rules education system.
- Implement the plan: Once the House of Quality has been developed, it is time to implement the plan. This involves developing and testing the product or service.
- Validate the product or service: The final step is to validate the product or service with customers. This involves ensuring that the product or service meets their needs.
Best Practices for QFD Implementation
- Engage stakeholders: It is important to engage all stakeholders in the QFD process. This includes customers, employees, suppliers, and management.
- Use data and analysis: It is important to use data and analysis to support decisions made in the QFD process.
- Be flexible: The QFD process should be flexible to adapt to changes in customer needs and market conditions.
Examples of QFD Use
QFD has been successfully used in a wide range of industries. Some examples of successful QFD case studies include:
- Food production: de Fátima et al., (2015) report the application of Quality Function Deployment in the development of a natural fruit jelly.
- Construction: Wood et al., (2016) employed QFD in the design process of an eco-friendly hospital.
- Materials analysis: Kasaei et al., (2014) highlight that QFD can be employed in material selection for engineering.
QFD and Other Methodologies
QFD and Lean Manufacturing
QFD and Lean Manufacturing are two methodologies that can be used together to improve quality and efficiency. Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste from the production process, while Quality Function Deployment focuses on satisfying customer needs. By combining these two methodologies, companies can create high-quality products and services at lower cost.
Paharia (2024) investigated how QFD and Lean principles can create synergies to identify and eliminate waste in industrial processes; and reports that by systematically mapping customer requirements for process improvements and implementing Lean methodologies, organizations can optimize operations, resource utilization, and waste generation reduction.
QFD and Six Sigma
QFD and Six Sigma are two methodologies that can be used together to improve quality. Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation in the production process, while QFD focuses on satisfying customer needs. By combining these two methodologies, companies can create high-quality products and services with fewer defects.
Lestari and Dachyar (2020) employed Quality Function Deployment and Six Sigma to improve service quality to increase customer satisfaction, they transferred the voice of the customer to the House of Quality by using both tools.
QFD and Design Thinking
QFD and Design Thinking are two methodologies that can be used together to develop innovative products and services. Design Thinking focuses on understanding user needs, while Quality Function Deployment focuses on translating those needs into product and service features. By combining these two methodologies, companies can create products and services that better meet customer needs.
Dharmawan et al., (2023) developed a design process for a COVID-19 patient monitoring system, which was carried out using a design thinking approach consisting of an empathy, definition, ideation, prototyping, and testing process, and the QFD method.
Resources to Learn More about Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Websites
Conclusion
In conclusion, Quality Function Deployment emerges as a fundamental methodology for companies striving to achieve excellence in product quality and customer satisfaction. By prioritizing customer needs, using solid tools and methodologies, and fostering a culture of innovation, organizations can harness the power of QFD to drive success in today’s competitive landscape. Adopting Quality Function Deployment is not simply a strategic choice; it is a commitment to delivering products that resonate with customers and stand the test of time.
QFD is a powerful methodology that can help companies improve quality, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction. Quality Function Deployment can be used in a wide range of industries and can be combined with other methodologies to further improve results.
QFD is a methodology that continues to evolve. As customer needs and market conditions change, Quality Function Deployment will adapt to remain a valuable tool for companies.
References
Buics, L., Horváth, Z. C., Földesi, P., & Eisinger, B. B. (2024). An assessment of traffic education and its examination system—an extended House of Quality approach. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 1-13.
Dharmawan, M. A., Mufidah, I., Martini, S., & Akbar, M. D. (2023). The Development of Patient Monitoring System Application: Integrating Design Thinking and QFD Method. International Journal of Social Service and Research, 3(6), 1452-1461.
de Fátima Cardoso, J., Casarotto Filho, N., & Miguel, P. A. C. (2015). Application of Quality Function Deployment for the development of an organic product. Food Quality and Preference, 40, 180-190.
Erdil, N.O. and Arani, O.M. (2019), “Quality function deployment: more than a design tool“, International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 2, pp. 142-166. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJQSS-02-2018-0008
Ginting, R., Ishak, A., Malik, A. F., & Satrio, M. R. (2020, December). Product development with quality function deployment (QFD): a literature review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 1003, No. 1, p. 012022). IOP Publishing.
Jaiswal, E. S. (2012). A case study on quality function deployment (QFD). Journal of mechanical and civil engineering, 3(6), 27-35.
Kasaei, A., Abedian, A., & Milani, A. S. (2014). An application of Quality Function Deployment method in engineering materials selection. Materials & Design, 55, 912-920.
Klochkov, Y., Klochkova, E., Volgina, A., & Dementiev, S. (2016, February). Human factor in quality function deployment. In 2016 Second International Symposium on Stochastic Models in Reliability Engineering, Life Science and Operations Management (SMRLO) (pp. 466-468). IEEE.
Lestari, D. P., & Dachyar, M. (2020). Improvement of service quality for customer satisfaction with lean six sigma method and development quality function deployment. Case: Telecommunication company in indonesia. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol, 29, 3605-13.
Paharia, C. K. (2024). OPTIMIZING INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES: THE SYNERGY OF QUALITY FUNCTION DEPLOYMENT (QFD) AND LEAN PRINCIPLES IN WASTE REDUCTION. IFSMRC African international Journal of Research in Management, 12(02), 01-07.
Wood, L. C., Wang, C., Abdul-Rahman, H., & Abdul-Nasir, N. S. J. (2016). Green hospital design: integrating quality function deployment and end-user demands. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 903-913.
Xiao, J., & Wang, X. (2024). An optimization method for handling incomplete and conflicting opinions in quality function deployment based on consistency and consensus reaching process. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 187, 109779.
Zare Mehrjerdi, Y. (2010), “Quality function deployment and its extensions“, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 27 No. 6, pp. 616-640. https://doi.org/10.1108/02656711011054524