The success of any business depends on customer satisfaction. The Kano model is a powerful tool that helps companies understand their customers’ needs and develop products and services that meet those needs.
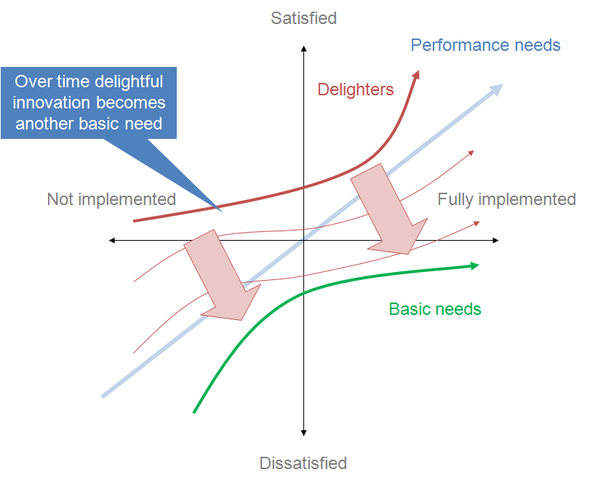
The Kano model focuses on differentiating between basic and delightful features that impact customer satisfaction. By categorizing customer preferences into five distinct levels, the model helps companies prioritize which features to focus on to improve customer satisfaction.
By incorporating the Kano model into their marketing and product development strategies, companies can gain deep insights into customer expectations, leading to more specific and customer-focused decision-making. Ultimately, this improves customer satisfaction and helps build long-term relationships with customers.
In this article, we will delve into the power of the Kano Model and explore how it can revolutionize the way your company approaches customer satisfaction. Unlock the power of the Kano model and take your customer experience to new heights!
Understanding Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is key to building a successful and sustainable business. When customers are satisfied, they are more likely to return to purchase products or services, recommend them to others, and become loyal brand advocates. However, understanding what truly satisfies customers can be challenging.
According to Rotar and Kozar (2017), the interest in measuring customer satisfaction is reflected in its ability to gain loyalty, improve favorable word-of-mouth, generate repeat purchases, and improve a company’s market share and profitability.
Traditional customer satisfaction surveys often fail to provide accurate information about customer preferences. Customers may not always be able to express what they want, or they may not even be aware of their own expectations. This is where the Kano Model can make a significant difference.
What is the Kano Model?
The Kano model was developed by Dr. Noriaki Kano, a quality management professor at the Tokyo University of Science, in the 1980s. It is a powerful tool that helps companies understand customer preferences and prioritize features to improve satisfaction.
According to Slevitch, L. (2024), although the original categorization framework remains the most applied, modifications and new approaches have recently been developed. Thus, the Kano analysis model is a framework for classifying product or service features into five categories: basic requirements, performance, exciters, indifferent, and questionable.
- Basic requirements: Essential or minimum features that customers expect and take for granted from a product or service; often include fundamental functionalities that customers consider essential. If these features are not present, the customer will be dissatisfied.
- Performance: These features are directly proportional to customer satisfaction. The better a product or service performs in these areas, the more satisfied the customers will be. Improving performance requirements can generate customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
- Exciters: Features that exceed customer expectations and generate delight. These features are what make a product or service stand out from the competition, they are unexpected or innovative elements that delight customers. Excitement requirements have the potential to create a competitive advantage and differentiate a brand from its competitors.
- Indifferent: Features that are not important to the customer. They do not have a significant impact on customer satisfaction.
- Questionable: Features that can cause dissatisfaction if implemented incorrectly. It is important to be cautious when implementing these features.
These five categories of product or service features can be grouped into Include and Avoid.
Table 01. Grouping of the five categories of the Kano analysis model based on their inclusion.
| Features to Include | Features to Avoid |
| Basic Requirements Performance Exciters | Indifferent Questionable |
Benefits of the Kano Model
The Kano model offers several benefits for businesses, including:
- Product or Service Design: The Kano model is a technique used in product development to identify the most suitable combination of features to maximize product satisfaction (Dalton & Dalton, 2019).
- Improves Customer Satisfaction: By understanding customer needs, companies can develop products and services that better meet those needs.
- Increases Customer Retention: Customers who are satisfied with a product or service are more likely to continue using it.
- Reduces Costs: By identifying features that are not important to the customer, companies can avoid spending money on developing or implementing them.
- Enhances Competitiveness: Companies using the Kano model can develop products and services that are more competitive in the market.
Applications of the Kano Model
The Kano model can be used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Product Development: The Kano model can identify features that customers desire in a new product. Integrating the Kano analysis model with Quality Function Deployment (QFD) can enable innovative requirements to receive necessary attention in the product development process (Tontini, 2007).
- Product Improvement: The Kano model can identify features of an existing product that can be improved to increase customer satisfaction.
- Service Development: The Kano model can identify features that customers desire in a new service. For example, Cavacece et al. (2024) demonstrate the effectiveness of the Kano model in evaluating the nonlinear correlation between user satisfaction and the quality of digital health services.
- Improving Customer Service: The Kano model can be used to identify areas where customer service can be improved. Rotar and Kozar (2017) employed the Kano analysis model in appliance marketing, recommending that marketers should focus on pleasure features, such as broader knowledge of the seller, professional skills of the seller, appliance design, and appliance brand.
Using the Kano Analysis Model in Product Development
In product design and development, there are many methods that can be used, one of which is using the Kano model (Ishak et al., 2020). This model can be applied at various stages of product development to ensure that customer satisfaction remains a priority. By understanding the different categories of customer requirements, companies can make informed decisions about which features to prioritize and invest resources in.
In the ideation and concept development stage, the Kano model can help identify potential attractive requirements that could differentiate a product from competitors. By incorporating innovative and new built-in features, companies can create a sense of excitement and anticipation among customers.
During the design and development stage, the Kano model can guide the team to prioritize features based on their impact on customer satisfaction. By focusing on basic and one-dimensional requirements, companies can ensure that the core functionalities of the product meet customer expectations.
Kano Model for Prioritizing Product or Service Features
One of the key advantages of the Kano model is its ability to help companies prioritize features based on their impact on customer satisfaction. By analyzing customer preferences and categorizing features into the different levels of the Kano Model, companies can make informed decisions about where to allocate resources and efforts.
Features categorized as basic requirements should be prioritized, as they form the foundation of customer satisfaction. Failing to meet these basic expectations can lead to significant dissatisfaction and even drive customers to seek alternatives.
Performance requirements should also be prioritized, as they have a direct impact on customer satisfaction. By improving performance in these areas, companies can enhance customer satisfaction and build loyalty. Exciting requirements should not be overlooked, even though they are not essential. These features have the potential to surprise and delight customers, creating positive emotional connections and differentiating the brand from competitors.
How to Perform a Kano Analysis
The Kano Model is an invaluable tool for understanding customer preferences and expectations regarding a product or service. Here’s a step-by-step guide to applying the Kano Model:
Step 1: Understand the Elements of the Kano Model
According to Sharif and Tamaki (2011), in the Kano model, customer preferences are obtained using a prescribed method to determine whether a given product attribute is a basic (must-have), performance (linear), attractive (exciters), indifferent, or reverse (questionable) attribute for a given product. Below is a brief description:
- Basic Attributes: These are fundamental characteristics of the product or service that are expected and taken for granted. Their absence leads to dissatisfaction, but their presence does not necessarily generate additional satisfaction.
- Performance Attributes (Linear): These are characteristics that show a direct relationship between their presence and customer satisfaction. The more they are improved, the higher the customer satisfaction.
- Exciting Attributes: These are unexpected features that generate great satisfaction when present but do not cause dissatisfaction when absent, as customers do not expect them.
- Indifferent Attributes: These are features that do not have a significant impact on customer satisfaction, either because they are not used much or because their presence or absence is not perceived as important.
- Questionable Attributes (Reverse): These are features that, when present, cause dissatisfaction, but their absence does not necessarily generate satisfaction.
Step 2: Identify Attributes
- List Features: List all features of the product or service you are evaluating.
- Classify Features: Classify each identified feature into one of the five categories of the Kano Model.
Step 3: Collect Data
- Customer Surveys: Use surveys to collect data on customers’ perception of the product or service features (Appendix 01: Example survey to evaluate video streaming subscription service).
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to determine the classification of each attribute in the Kano Model.
Step 4: Interpret Results
- Prioritize Attributes: Identify basic attributes that must be met to avoid customer dissatisfaction. Then prioritize linear and exciting attributes to improve customer satisfaction.
- Identify Opportunities: Look for opportunities to differentiate your product or service by enhancing exciting attributes and eliminating or mitigating reverse attributes.
Step 5: Implement Changes
- Develop Strategies: Develop strategies to improve linear and exciting attributes and to address identified reverse attributes.
- Testing and Validation: Implement changes to the product or service and conduct tests to ensure they align with customer expectations and preferences.
Step 6: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
- Customer Satisfaction Monitoring: Continue collecting data on customer satisfaction to assess the impact of implemented changes.
- Iteration: Use the obtained results to make additional adjustments to the product or service, ensuring that it continues to meet the needs and expectations of customers.
By effectively applying the Kano Model, you can develop products and services that not only meet customer expectations but also surprise and delight them, thereby generating loyalty and competitive advantage.
Examples of Using the Kano Model
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the Kano Model in improving customer satisfaction. Let’s take a look at some examples:
Healthcare Services
Materla et al. (2019) implemented the Kano model to identify a wide range of complex patient needs and convey its potential utility in the continuous improvement of the healthcare sector. They report that out of the 21 quality attributes evaluated by patients, 16 were categorized as one-dimensional, 3 as indifferent, and 2 as attractive.
Retail Sector
Kermanshachi et al. (2022) identified, categorized, and classified attributes of retail stores based on their effects on customer satisfaction. They report that visually appealing facilities and error-free transactions are of paramount importance to customers.
Higher Education
Madzík et al. (2019) explored possibilities for improving understanding of customer and stakeholder requirements in the process of creating products in educational services based on seven general requirements. They highlight that “practice orientation” and “quality resources” are the most stable requirements, while “quality staff” is the least stable. The most linear requirement found by researchers is “innovation orientation.”
Hotel Service
Hotel service is one of the most competitive in the world. Andriani et al. (2021) identified customer dissatisfaction with the quality of hotel services and provided design proposals to improve service quality. They identified 18 attributes as proposed designs to enhance service quality, five of which are adding and completing service-related equipment, improving infrastructure, improving and developing standard operating procedures (SOP), periodic maintenance and replacement of service support equipment, acquisition of cleaning service equipment, cleaning of facilities and infrastructure, installation of signs, notices, and information.
These case studies highlight the power of the Kano Model to guide companies towards customer-centric decision-making and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Limitations of the Kano Model
While the Kano model offers valuable insights into customer preferences and satisfaction, it is not without challenges and limitations. It is important to be aware of these limitations to ensure effective implementation of the model.
One challenge is the subjective nature of categorizing features into the different levels of the Kano Model. Different customers may have different expectations and interpretations of what constitutes basic, performance, or excitement requirements. It is crucial to gather diverse feedback from customers.
Conclusion
The Kano model is a powerful tool that helps companies understand their customers’ needs and develop products and services that meet those needs. By using the Kano model, companies can improve customer satisfaction, increase customer retention, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness.
Bibliographic References
Andriani, M., Irawan, H., & Asyura, N. R. (2021). Improving Quality Using The Kano Model in Overcoming Competition in The Service Industry. International Journal of Engineering, Science and Information Technology, 1(4), 13-18.
Cavacece, Y., Maggiore, G., Resciniti, R. and Moretta Tartaglione, A. (2024), “Evaluating digital health attributes for users’ satisfaction: an application of the Kano model“, The TQM Journal, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-09-2023-0301
Dalton, J., & Dalton, J. (2019). Kano model. Great Big Agile: An OS for Agile Leaders, 189-190.
Ishak, A., Ginting, R., Suwandira, B., & Malik, A. F. (2020, December). Integration of kano model and quality function deployment (QFD) to improve product quality: a literature review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 1003, No. 1, p. 012025). IOP Publishing.
Kermanshachi S, Nipa TJ, Nadiri H (2022) Service quality assessment and enhancement using Kano model. PLoS ONE 17(2): e0264423. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264423
Madzík, P., Budaj, P., Mikuláš, D., & Zimon, D. (2019). Application of the Kano Model for a Better Understanding of Customer Requirements in Higher Education—A Pilot Study. Administrative Sciences, 9(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010011
Materla, T., Cudney, E.A. and Hopen, D. (2019), “Evaluating factors affecting patient satisfaction using the Kano model“, International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance, Vol. 32 No. 1, pp. 137-151. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHCQA-02-2018-0056
Rotar, L. J., & Kozar, M. (2017). The use of the Kano model to enhance customer satisfaction. Organizacija, 50(4), 339-351.
Sharif Ullah, A. M. M., & Tamaki, J. I. (2011). Analysis of Kano‐model‐based customer needs for product development. Systems Engineering, 14(2), 154-172.
Slevitch, L. (2024). Kano Model Categorization Methods: Typology and Systematic Critical Overview for Hospitality and Tourism Academics and Practitioners. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 10963480241230957.
Tontini, G. (2007). Integrating the Kano model and QFD for designing new products. Total Quality Management, 18(6), 599-612.
Annex 01: Example Survey for Video Streaming Service Feature Evaluation
Dear Customer,
Thank you for participating in our survey to improve our video streaming service. Your feedback is invaluable to us. Please take a few minutes to complete this questionnaire. The responses you provide will help us better understand your needs and expectations.
Instructions:
Read each feature listed below and rate its importance and satisfaction based on your current experience with the service.
Use the following rating scale for each feature:
1: Not important / Not satisfied
2: Indifferent / Somewhat satisfied
3: Important / Satisfied
4: Very important / Very satisfied
5: Exciter / Extremely satisfied
Features:
1. Wide variety of content:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
2. Video streaming quality (resolution, smoothness):
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
3. Personalized content recommendations:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
4. Availability of offline content:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
5. Ease of use of the user interface:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
6. Content search and filtering functionality:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
7. Frequent content updates:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
8. Effective customer service and technical support:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
9. Seamless playback experience (no buffering):
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
10. Exclusive offers and additional content for premium subscribers:
Importance: [ ]
Satisfaction: [ ]
Please mark an “X” on the importance and satisfaction scale for each feature. Additionally, if there is any feature you would like to mention that has not been included in this list, please indicate it below:
[Space for additional comments:]
Thank you for your time and feedback!
Note: This sample survey provides a structured way to collect data on customer preferences and satisfaction regarding various features of the video streaming service. The results of this survey can then be analyzed and classified using the Kano Model to identify priority improvement areas and opportunities.
Annex 02: Survey Data Analysis in the Kano Model for Video Streaming Service
Here is an example of data analysis based on the survey responses presented in Annex 01.
Step 1: Response Tabulation
First, tabulate the responses from all surveys, assigning each feature an importance and satisfaction score according to the scale provided in the survey.
| Feature | Importance (Average) | Satisfaction (Average) |
|---|---|---|
| Wide variety of content | 4.2 | 3.8 |
| Video streaming quality | 4.5 | 4.0 |
| Personalized recommendations | 3.8 | 3.5 |
| Availability of offline content | 3.6 | 3.7 |
| Ease of use of the interface | 4.3 | 4.1 |
| Search functionality | 4.0 | 3.9 |
| Frequent updates | 4.1 | 3.8 |
| Customer service | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| Playback experience | 4.4 | 4.2 |
| Exclusive offers | 3.9 | 3.6 |
Step 2: Classification in the Kano Model
Using the importance and satisfaction scores, classify each feature into one of the categories of the Kano Model:
- Exciters: Features with high importance and high satisfaction.
- Linears: Features with high importance but variable satisfaction.
- Basics: Features with high importance but low satisfaction.
- Indifferent: Features with low importance and variable satisfaction.
| Feature | Classification |
|---|---|
| Wide variety of content | Exciter |
| Video streaming quality | Linear |
| Personalized recommendations | Linear |
| Availability of offline content | Linear |
| Ease of use of the interface | Linear |
| Search functionality | Linear |
| Frequent updates | Linear |
| Customer service | Linear |
| Playback experience | Linear |
| Exclusive offers | Linear |
Step 3: Interpretation and Recommended Actions
- Exciters: The wide variety of content is a feature that generates high satisfaction among customers and should be further promoted to maintain competitive advantage.
- Linears: Features such as video streaming quality and ease of use of the interface are important but can be improved to increase customer satisfaction.
- Basics: Customer service shows low satisfaction compared to its importance, indicating the need to improve this aspect to avoid customer dissatisfaction.
- Indifferent: There are no features classified as indifferent in this example.
Step 4: Improvement Planning and Strategies
- Implement measures to improve video streaming quality and ease of use of the interface.
- Provide additional training to customer service staff and enhance communication channels to resolve issues more effectively.
- Continue focusing on expanding the variety of content to maintain customer enthusiasm.
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.