In the ever-evolving landscape of Industry 4.0, the concept of digital twins has emerged as an innovative technology promising more accurate and reliable representations of assets and processes.
However, despite their potential, the development of digital twins has faced various challenges, including their adaptation to specific environments and the need for seamless integration of technologies such as machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 3D visualization.
These challenges can limit the scalability and accessibility of digital twin solutions, prompting the need for an open-source framework that simplifies the creation and orchestration of advanced digital twins.
In this context, three engineers from the ERTIS research group at the University of Malaga have developed an open-source platform that is more accessible and versatile, allowing the design of technological tools that simulate real environments based on virtual replicas.
We refer to ‘Open Twins,’ the first integrated open-source ecosystem of ‘digital twins,’ capable of combining the latest technologies: Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), monitoring, simulation models, and 3D visualization. The source code is fully available on GitHub.
Digital Twins: A Brief Description
Defined as “dynamic and digital representations of a real object, process, or system capable of imitating and analyzing its behavior,” the researchers from UMA, authors of this study, explain that although the term “digital twin” first appeared in 2010, it was not until about five years ago that it gained widespread use.
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical objects, systems, or processes. These twins allow us to monitor, analyze, and simulate real-world assets, which can be invaluable for various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation.
The ability to create these virtual representations has the potential to revolutionize how we manage and optimize complex systems.
The Current Landscape of Digital Twins
Existing digital twin solutions in the market often cater to specific environments, making them less adaptable to broader applications. Furthermore, the integration of essential technologies like machine learning, IoT data streams, and 3D visualization can be challenging due to the lack of seamless alignment in open-source solutions.
“So far, most existing platforms of this kind have been non-modifiable paid platforms,” emphasizes Manuel Díaz, professor at the Faculty of Computer Science at UMA and director of the Ada Byron Research Center, who states that “Open Twins” overcomes these limitations and, in addition, adds “composability,” meaning it allows ‘twins’ to connect with each other more easily, achieving more complex structures.
This can result in a fragmented ecosystem, hindering the development and implementation of advanced digital twins.
“Currently, system simulation and modeling are indispensable tools in many industries, such as manufacturing and automotive, as they can predict how real systems would perform in different situations, preventing risks,” adds Cristian Martín, professor at the Department of Computer Science and Programming Languages.
A Glimpse into the Solution
To address these challenges, a novel open-source framework for the development of compositional digital twins has been introduced. These digital twins, as their name suggests, allow the linkage of individual entities or subsystems to create a higher-level digital twin. This interconnected approach facilitates knowledge sharing and data relationships, making it a powerful tool for industries striving to optimize their processes.
A Real-World Demonstration
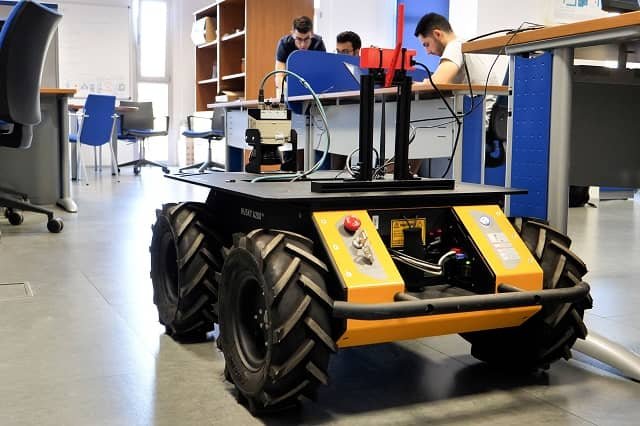
Real-world applications of “digital twins” created by engineers from the “ERTIS” group at UMA include an agricultural project measuring the accuracy of an irrigation plan, developed in collaboration with the University of Córdoba; a robot communicating via 5G technology to control movement on the “La Mayora” experimental farm, predicting fruit ripening and optimal maturity; and a predictive model developed for the Petrochemical Industry 4.0.

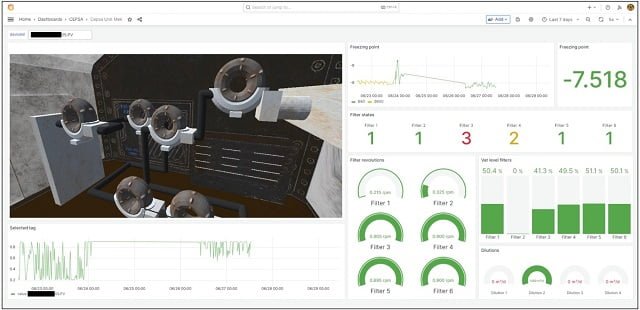
To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed framework, a use case has been developed in the context of Petrochemical Industry 4.0. In this scenario, the framework has been employed to create advanced digital twins representing various components within the industry.
These digital twins enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making, ultimately improving the efficiency and reliability of the entire operation.
The Future of Compositional Digital Twins
The introduction of an open-source framework for compositional digital twins is a significant step toward a more accessible and scalable digital twin ecosystem. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see its adoption in a wide range of industries, further optimizing processes, reducing downtime, and enhancing decision-making capabilities.
Conclusion
“In this article, we propose an open-source platform for the development of compositional digital twins that can adapt to multiple contexts. We refer to digital twins that can seamlessly integrate with predictive models through the Kafka-ML open platform, interactive digital twins provided through Unity support for 3D representations, and a unified interface for straightforward real-time IoT monitoring data visualization and complex models,” concluded the researchers.
The era of Industry 4.0 is just around the corner, and compositional digital twins are poised to play a fundamental role in this transformative journey. By providing an open framework that simplifies their development and orchestration, we are unlocking the full potential of digital twins, creating a future in which these virtual replicas are readily available to industries seeking to harness their power for a more efficient and sustainable future.
The study was funded by the Spanish projects ‘5G+TACTILE_2: Digital Vertical Twins for B5G/6G Networks,’ ‘SIERRA: Application of Digital Twins to More Sustainable Irrigation Operations,’ ‘DiTaS: A Framework for Agnostic Cognitive and Compositional Digital Twin Services,’ and ‘GEDERA: Intelligent and Flexible Management of Energy Demand in Coupled Hybrid Networks,’ as well as by open-access funding from the University of Malaga/CBUA.
Contact
Julia Robles
ITIS Software, University de Málaga, Arquitecto Francisco Peñalosa, 18, 29071 Málaga, España
Email: juliarobles@uma.es
Referencia (acceso abierto)
Julia Robles, Cristian Martín, Manuel Díaz. 2023. OpenTwins: An open-source framework for the development of next-gen compositional digital twins, Computers in Industry, Volume 152, 2023, 104007, ISSN 0166-3615, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2023.104007.