In today’s rapidly evolving world, technological innovation is a driving force behind progress and development. It encompasses the process of developing and implementing new technologies that can enhance the way we live and work, serving as a key engine of economic growth and social progress. However, the rapid pace of technological change also contributes to creating a highly competitive environment for businesses.
The UNCTAD’s “Technology and Innovation Report 2021: Catching Technological Waves” highlights the tremendous potential of frontier technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology for sustainable development. Yet, it also underscores the risk of exacerbating inequalities and urges all developing nations and their enterprises to prepare for a period of profound and rapid technological change.
In this context, there is a growing global interest in promoting innovative activity among companies to maintain or increase the competitiveness of local industries. In this article, we will explore the meaning of technological innovation, its benefits, and how companies can develop and implement successful innovation strategies.
Meaning of Technological Innovation
Technological innovation encompasses the creation, adoption, and utilization of new technologies to improve processes, products, or services. It represents a continuous journey of discovery and advancement, driven by human ingenuity and the pursuit of efficiency and excellence. In essence, technological innovation seeks to push boundaries, challenge conventions, and revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
What is Technological Innovation?
According to the OECD, technological innovation comprises new or significantly modified technological products and processes where technological novelties emerge. In other words, a company innovates when it brings new products to the market or improves existing ones.
In a more general sense, technological innovation is the process of developing and implementing new technologies that can improve the way we live and work. It may involve the development of new products, services, or processes. Innovation can be incremental, involving small improvements to existing technologies, or radical, involving the development of entirely new technologies.
As highlighted by Aponte (2015), technological innovation does not occur instantaneously; it requires the implementation of knowledge, techniques, tools, and resources, which are part of a company’s innovation strategy.
Benefits of Technological Innovation
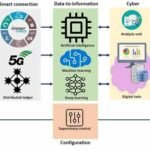
Technological innovation, within the framework of Industry 4.0, has socioeconomic, environmental, organizational, and political impacts, and is essential for cost reduction and survival in local and foreign markets. In this framework, technological innovations generate the following benefits:
- Economic Growth: Technological innovation leads to the development of new products and services, which can generate new industries and jobs, resulting in greater economic growth and prosperity. Research by Zhong and Chen (2023) indicates that technological innovation plays a partial mediating role in the impact of the business environment on high-quality economic development.
- Social Progress: Technological innovation can improve the quality of life by providing access to better products and services, such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Increased Productivity: Technological innovation can help businesses become more efficient and productive, leading to lower costs and higher profits.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Companies that innovate are more competitive in the global market, helping them attract and retain customers and employees. Dwivedi et al. (2023) emphasize that technological innovation fosters the development of sustainable practices in manufacturing sectors, based on entrepreneurship direction toward innovation and market direction toward innovation.
- Improved Quality of Life: Technological innovation can enhance the quality of life by providing access to better products and services, such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
Types of Technological Innovation
There are many classifications of types of technological innovation; however, for this article, we summarize what Kylliäinen (2019) proposes, which defines four types of technological innovation:
Radical
Radical innovation is rare and characterized by employing revolutionary technology and a new business model. Radical innovations solve global problems and respond to needs in completely new ways. The goal of radical innovation is to exceed the performance threshold rather than serve underserved markets.
Incremental
Incremental innovations are only small improvements on previous versions of a product or service. This type of innovation is built on the existing technological competencies of the company and with the same business model. Although incremental innovation does not create new markets, it can attract customers who pay more because it meet customer needs. This type of innovation is practiced by leading companies worldwide.
Disruptive
Disruptive innovation refers to a concept, product, or service that creates a new value chain by entering an existing market or creating a completely new market. This type of innovation requires a new business model and challenges the business models of other companies.
Sustainable
Sustainable innovation aims to improve and grow in current markets by meeting customer needs. Sustainable innovation is a significant improvement in a product aimed at maintaining a position in an existing market.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that there are types of non-technological innovation such as social innovation, frugal innovation, or public innovation.
Technological Innovation in Companies
The importance of technological innovation for creating value in companies has made its management a fundamental and strategic part of business activity. Moughari and Daim (2023) highlight that technological innovation is one of the most effective ways for companies to gain a competitive advantage and improve their competitiveness.
Companies innovate as a result of market demand, and initially, innovation processes begin with the review and combination of all existing knowledge, involving user innovation and the use of information as important sources of innovation (Diaconu, 2011). However, interactions with customers, suppliers, competitors, and public and private organizations are important to initiate innovation processes.
Although technological innovations can be accidental or planned, many companies seek, and must, manage them to make innovation more profitable for the company. According to Pérez (2017), the main characteristics of an innovative company are efficiency, competitiveness, and quality; furthermore, an innovative company must be able to create or renew products, services, and even the production techniques it uses (Pérez, 2017).
On the other hand, when we talk about technological innovations, frontier technologies are not always the most suitable for all companies; this will depend on different aspects. However, low-tech innovations can be a good tool for addressing global challenges (Hartley et al., 2019).
Management of Technological Innovation
The management of technological innovation has become one of the main challenges facing managers today.
Innovation managers must know very well the context in which companies carry out their activities. In this way, managers need to understand their companies’ positions within the business environment and innovation systems.
Likewise, managers need to understand how the innovation process is changing and where the company can search among the different sources of innovation.
It is important to highlight that companies are not an island, and therefore they must adopt open innovation models.
Development and Implementation of a Successful Innovation Strategy
Developing a solid technological innovation strategy is imperative for organizations seeking to thrive in a constantly changing landscape. It involves aligning business objectives with technological capabilities, fostering a culture of experimentation and collaboration, and investing in research and development initiatives.
The implementation of technological innovation involves a large number of important strategic decisions (Plinta and Radwan, 2023); likewise, Zou (2024) indicates that the technological innovation process can be divided into five stages: introduction of innovation in new technologies, architectural innovation, standardization, integration, and paradigm shift. In this context, the development and implementation of an innovation strategy in a company includes:
- Creating a culture of innovation: It is important to create an environment where employees feel comfortable taking risks and being creative.
- Investing in research and development: It is important to invest in research and development to develop new technologies.
- Fostering employee creativity: It is important to foster employee creativity by providing opportunities for learning and growth.
- Encouraging collaboration: It is important to encourage collaboration among employees, departments, and organizations in the same sector and environment. Li et al. (2024) found that high-tech companies that carry out cooperative innovation can effectively improve their performance in technological innovation.
- Protecting intellectual property: It is important to protect intellectual property to prevent competitors from copying ideas.
Examples of Technological Innovation
Technological innovations, and their applications, are emerging in all human activities. We have technologies that are being applied in agriculture, industry, biotechnology, and fishing, among other economic sectors.
Technological innovations can provide significant reductions in carbon emissions, for example through energy-efficient applications and equipment, such as electric vehicles and energy-efficient lighting (LEDs). Here is a list of examples of technological innovations and their fields of application:
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing many aspects of our lives. It is being used to develop applications such as:
- Virtual assistants: like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Process automation: to automate repetitive tasks in work and home.
- Facial recognition: to unlock devices, make payments, and enhance security.
- Automatic translation: to translate languages in real-time.
- Medical diagnosis: to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately.
2. Big Data: Big data refers to the large amount of data generated from different sources, such as the internet, social networks, and sensors. It is being used to develop applications such as:
- Market analysis: to better understand customer needs and develop more relevant products and services.
- Price optimization: to adjust product prices based on demand and competition.
- Fraud detection: to identify and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Predictive maintenance: to predict when equipment will fail and take preventive measures.
- Personalization: to offer customers personalized experiences.
3. Robotics: Robotics is being used to develop robots that can perform tasks previously done by humans, such as:
- Manufacturing: to assemble products more efficiently and accurately.
- Logistics: to move and store products in warehouses.
- Healthcare: to perform surgeries and provide care to patients.
- Agriculture: to plant, harvest, and cultivate food.
4. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of physical objects connected to the internet that can collect and share data. It is being used to develop applications such as:
- Smart homes: to control home lighting, temperature, and security.
- Smart cities: to improve traffic management, lighting, and energy in cities.
- Smart agriculture and livestock farming: to monitor crops and livestock.
- Healthcare: to monitor patients’ health remotely.
- Industry 4.0: to connect machines and optimize production.
5. 3D Printing: 3D printing is being used to create three-dimensional objects from digital files. It is being used to develop applications such as:
- Prototyping: to quickly and inexpensively create product prototypes.
- Custom manufacturing: to create custom products for each customer.
- Organ printing: to create human organs for transplants.
- Food printing: to create personalized and nutritious foods.
- Construction: to build houses and buildings more efficiently.
6. Blockchain: Blockchain is a technology that allows for the creation of a secure and transparent record of transactions. It is being used to develop applications such as:
- Cryptocurrencies: like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Supply chain: to track the origin and authenticity of products.
- Digital identity: to create secure digital identities.
- Electronic voting: to enable people to vote securely and transparently.
- Insurance: to automate policy and claims management.
7. Biotechnology: Biotechnology is being used to develop applications such as:
- Personalized medicine: to develop personalized drugs and treatments for each patient.
- Sustainable agriculture: to develop crops more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Biofuels: to produce fuels from renewable sources.
- Nanomedicine: to develop new methods of disease diagnosis and treatment.
- Bioremediation: to clean up environmental pollution.
8. Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology is being used to develop applications such as:
- Faster and more efficient electronics: using smaller and more efficient transistors.
- New drugs: to combat diseases more precisely and effectively.
- Improvements in agriculture: to increase food production and reduce pesticide use.
- Water purification: to remove contaminants from drinking water.
- More efficient solar energy: to produce solar energy more efficiently and economically.
9. Renewable Energies: Renewable energies are being used to develop applications such as:
- Solar energy: to generate electricity from sunlight.
- Wind energy: to generate electricity from wind.
- Geothermal energy: to generate electricity from the heat of the earth.
- Hydropower: to generate electricity from water.
- Biomass: to generate energy from organic matter.
9. Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles are vehicles that can be driven without human intervention. They are being used to develop applications such as:
- Autonomous cars: which can safely and efficiently transport people.
- Autonomous trucks: which can safely and efficiently transport goods.
- Drones: which can be used for package delivery, surveillance, and agriculture.
- Delivery robots: which can be used to deliver food and other products to homes.
Conclusion
The importance of technological innovation in the 21st century cannot be overstated. Innovation is key to driving economic growth, social progress, and a better quality of life. Companies that can develop and implement successful innovation strategies will be well-positioned to succeed in the global market.
Currently, there are frontier technologies that business managers must start to know and adapt to keep their businesses current; however, there are also low-tech options that can allow your company to remain competitive in the local and international markets.
Finally, while the benefits of technological innovation are undeniable, managing the process presents its own set of challenges. From resource limitations to resistance to change, organizations must navigate various obstacles to ensure the successful implementation and adoption of new technologies. Effective innovation management requires strong leadership, clear communication, and a willingness to adapt and evolve in response to feedback and market dynamics.
References
Aponte Figueroa, Gloria María, y “EL PROCESO DE GESTIÓN DE INNOVACIÓN TECNOLÓGICA: SUS ETAPAS E INDICADORES RELACIONADOS.” Revista Venezolana de Análisis de Coyuntura XXI, no. 1 (2015):59-90. Redalyc,
Cannavacciuolo, L., Ferraro, G., Ponsiglione, C., Primario, S., & Quinto, I. (2023). Technological innovation-enabling industry 4.0 paradigm: A systematic literature review. Technovation, 124, 102733.
Deloitte. Tech Trends 2020.
Diaconu, Mihaela. (2011). Technological Innovation: Concept, Process, Typology and Implications in the Economy. Theoretical and Applied Economics. XVIII(2011). 127-144.
Dodgson M., D. Gann & A. Salter. 2008. The Management of Technological Innovation: Strategy and Practice. Oxford University Press. 402 p.
Dwivedi, A., Sassanelli, C., Agrawal, D., Gonzalez, E. S., & D’Adamo, I. (2023). Technological innovation toward sustainability in manufacturing organizations: A circular economy perspective. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 35, 101211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2023.101211
Hartley S., Carmen McLeod, Mike Clifford, Sarah Jewitt & Charlotte Ray (2019) A retrospective analysis of responsible innovation for low-technology innovation in the Global South, Journal of Responsible Innovation, 6:2, 143-162, DOI: 10.1080/23299460.2019.1575682
Kylliäinen, J. 2019. Types of Innovation – The Ultimate Guide with Definitions and Examples.
Li, X., Wang, Q., Shi, R., Wang, X., Zhang, K., & Liu, X. (2024). Impact of Cooperative Innovation on the Technological Innovation Performance of High-Tech Firms: A Dual Moderating Effect Model of Big Data Capabilities and Policy Support. Big Data, 12(1), 63-80.
Moughari, M. M., & Daim, T. U. (2023). Developing a model of technological innovation for export development in developing countries. Technology in Society, 75, 102338.
Pérez A. 2017. Innovación tecnológica, tipos y características principales. OBS Business School.
Plinta, D., & Radwan, K. (2023). Implementation of Technological Innovation in a Manufacturing Company. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106068
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). 2021. Technology and Innovation Report 2021: Catching technological waves. United Nations. 196 p.
Zhang, Z., & Xu, X. (2023). Sustainable financial risk, resources abundance and technological innovation: Evidence from resources abundance economies. Resources Policy, 83, 103559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103559
Zhong, Z. and Chen, Z. (2023), “Business environment, technological innovation and government intervention: influences on high-quality economic development“, Management Decision, Vol. 61 No. 8, pp. 2413-2441. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-08-2022-1073
Zou, T. (2024). Technological innovation promotes industrial upgrading: An analytical framework. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 70, 150-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2024.01.012
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.