Perhaps as an entrepreneur, you have felt constrained by the lack of resources to innovate, or you may be thinking that this matter of innovation is only for medium and large companies that have resources.
I regret to inform you that you are completely mistaken. Today, I’m going to talk to you about frugal innovation, a new approach that democratizes the innovation processes and is oriented towards companies with limited resources.
Frugal innovation is about ‘doing more with less’: finding creative and cost-effective solutions to address real-world problems. Whether it’s about creating affordable products, optimizing processes, or discovering new ways to reach customers, frugal innovation is a mindset that enables companies to achieve greater efficiency without compromising quality.
The concept of frugality has been applied in various domains, ranging from healthcare and transportation to energy and manufacturing (Dabić et al., 2022); and it can help promote sustainability and address global challenges, such as generating economic growth, addressing diverse social needs, and protecting the environment (Albert, 2022).
If you’re an entrepreneur, we will now discuss the characteristics of frugal innovation, and how to become a frugal innovator; we will delve into the world of frugal innovation and explore how companies from all industries are harnessing its power to drive success.
Frugal Innovation: The Future of Innovation
In recent years, frugal innovation has emerged as a relevant topic in social and academic discourse, with some researchers considering it the future of innovation management.
While the goal of innovation management is to create new concepts and move away from conventional solutions, frugal innovation allows for a rethinking of the nature of innovation. This type of innovation enables small companies with limited resources to develop innovations for customers in low-income countries.
Significance of Frugal Innovation
The frugal mindset originated in emerging markets, especially in India and China. Some researchers consider India to be a leading market for frugal innovation, while others see it as a “laboratory for frugal innovations” (Prathap, 2014). However, frugal innovation is also being implemented in developed countries.
Frugal innovations primarily stem from the context of low- and middle-income markets, and the COVID-19 pandemic scenario highlighted the importance of jugaad innovation in developing products and equipment to address the pandemic. In this regard, Corsini et al. (2021) argue that frugal innovation is a significant strategy in crisis response beyond emerging markets, and that digital manufacturing can be considered a key enabler of frugal innovation, both in its ability to produce frugal solutions and to support distributed networks of innovation actors.

Frugal Innovation: The Future of Innovation
In recent years, frugal innovation has positioned itself as a relevant topic in both social and academic discourse, with some researchers considering it to be the future of innovation management.
While the aim of innovation management is to create new concepts and move away from conventional solutions, frugal innovation allows for a reimagining of the nature of innovation. This kind of innovation enables small companies with limited resources to develop solutions that cater to the needs and specific requirements of markets, and are affordable enough to offer opportunities for customers to consume them.
The true challenge for frugal innovation lies in introducing something new or different using minimal resources (Koerich and Pellizzaro, 2019). This form of innovation is a way of thinking and acting in response to challenges.
In recent years, the growing scarcity and volatility of resources have been pressuring companies to adopt frugal innovation. In this context, Albert (2022) highlights that jugaad innovation can be described as inherently socially and economically sustainable, with ecological sustainability mostly not being the primary focus.
What is Frugal Innovation?
Frugal innovation, also known as “jugaad innovation”, is an approach that emphasizes simplicity, affordability, and accessibility. It involves finding innovative solutions to problems by utilizing limited resources and constraints as opportunities for creativity. Unlike traditional innovation, which often entails high costs and complex processes, frugal innovation focuses on achieving more with less.
The term ‘frugal’ derives from the word ‘jugaad,’ a colloquial Hindi term that translates to ‘an innovative solution,’ born out of ingenuity and resourcefulness. Jugaad is at the heart of frugal innovation, as it encourages entrepreneurs and companies to think outside the box and find unconventional solutions to challenges.
It’s important to note that in the innovators’ community, ‘frugal’ is associated with resource economy, simplicity, and clarity; it signifies saving, using money or supplies in a careful manner (Merriam, 2016). In this regard, Dabić et al. (2022) highlight that jugaad innovation is a solution with scarce resources (i.e., product, service, process, or business model) that is designed and implemented despite financial, technological, material, or other resource limitations.
On the other hand, Jugaad, at its core, is a new model of innovation, based on challenges. It means solving a customer’s problem in the most innovative way when their resources are limited (Khan, 2016).
Gupta and Wang (2009) define frugal innovation as ‘innovation that strives to create products, services, processes, and business models that are frugal in three aspects: frugal use of raw materials, frugal impact on the environment, and extremely low costs.’
In summary, jugaad innovation is the ability to generate significantly more business and societal value while significantly reducing the use of scarce resources (Radjou and Prabhu, 2013).
The terms ‘jugaad innovation,’ ‘frugal engineering,’ or ‘reverse innovation’ are commonly used interchangeably with frugal innovation.
Principles of Frugal Innovation
Frugal innovation is guided by several fundamental principles that help companies harness its power effectively. These principles include:
- Simplicity: Frugal innovation emphasizes simplicity in product design, manufacturing processes, and business models. By simplifying things, companies can lower costs and make their products and services more accessible to a broader customer base.
- Affordability: The goal of jugaad innovation is to create products and services that are affordable for customers across income levels. By focusing on affordability, companies can access new markets and reach a wider customer base.
- Sustainability: Frugal innovation promotes sustainability by encouraging companies to use resources efficiently and minimize waste. This benefits not only the environment but also helps reduce costs and increase long-term profitability.
- Flexibility: Jugaad innovation encourages companies to be flexible and adaptable in their approach. This enables them to quickly respond to changing market conditions and customer needs, providing them with a competitive advantage.
On their part, in their book Radjou et al. (2012) establish six principles that characterize frugal innovation:
- Seek opportunity in adversity.
- Do more with less.
- Think and act flexibly.
- Keep it simple.
- Include the margin.
- Follow your heart.
Benefits of Adopting Frugal Innovation in Business
Adopting frugal innovation in businesses can yield several benefits, including:
- Cost savings: Frugal innovation allows companies to achieve more with less, resulting in significant cost savings. By finding creative and cost-effective solutions, companies can reduce production costs, optimize processes, and offer affordable products and services to customers.
- Market expansion: Jugaad innovation enables companies to access new markets and reach a wider customer base. By creating affordable and accessible products and services, companies can meet the needs of customers who were previously underserved.
- Increased competitiveness: Frugal innovation provides companies with a competitive advantage by enabling them to offer quality products and services at affordable prices. This helps them stand out in the market and attract customers who value affordability and simplicity.
- Environmental sustainability: Jugaad innovation promotes sustainable practices by encouraging companies to use resources efficiently and minimize waste. This not only benefits the environment but also helps companies reduce their carbon footprint and enhance their reputation as socially responsible organizations.
Criteria for Identifying Jugaad Innovation
All frugal solutions are characterized by affordability, ease of use, scalability, and an appealing value proposition. In this regard, Weyrauch and Herstatt (2016) established three criteria to define if an innovation is frugal:
a) Substantial reduction in costs
b) Focus on core functionalities
c) Optimization of performance level
On the other hand, from a business perspective, Prabhu J. (2017) highlights that to achieve their goals, companies have had to adopt the frugal innovation approach in a variety of activities, including:
a) how they source raw materials and manage their factories and supply chains,
b) how they design and package their products, and
c) how they engage with consumers to make them more environmentally conscious in their consumption behavior.
The Path of the Frugal Innovator
In his research, Hossain (2020) describes how frugal innovation unfolds, identifies its antecedents, illustrates how innovations spread, and highlights the outcomes of frugal innovations. Below is a summary of the main ideas from the researcher:
Antecedents
The researcher identified a group of initiators of Jugaad innovation:
- Potential customers for a new type of product encourage individuals to seek frugal innovation.
- Some individuals are socially isolated due to their race, skin color, ethnicity, religion, etc., consequently prompting them to find solutions to meet their personal and social needs.
- Cultural aspects play a significant role in frugal innovation, and many innovations arise from prevailing societal injustices.
Experiments
Entrepreneurs begin experimenting with their ideas once they realize their potential, and each experiment involves considering numerous decisions.
A key trait of an entrepreneur is the tenacity to turn an idea into a viable product. They take risks.
Diffusion
Once entrepreneurs have developed products ready for the market, the challenge is to spread the product within their target market.
Frugal products are easily marketed in local markets because they have been specifically developed to meet local needs.
After achieving success at the local level, frugal products can spread to other geographically adjacent markets.
Outcomes
Frugal products are affordable, sustainable, resource-efficient, and create a new market for new customers with a new type of product. They are also accessible to some customers who cannot afford equivalent conventional products.
Jugaad innovations are robust, user-friendly, and environmentally friendly, and are strongly linked to sustainability concerns.
Tools and Resources for Implementing Frugal Innovation
Implementing frugal innovation requires access to the right tools and resources. Here are some resources that can help you get started:
International Centre for Frugal Innovation
The International Centre for Frugal Innovation is an online platform that provides resources, case studies, and tools for implementing Jugaad innovation in business. It offers practical information and guidance to help you navigate the landscape of frugal innovation.
Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that can be applied to frugal innovation. It emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and experimentation, making it a valuable tool for generating innovative ideas.
Lean Startup Methodology
The Lean Startup methodology, popularized by Eric Ries, is another valuable resource for implementing frugal innovation. It emphasizes the importance of iterative development, customer feedback, and rapid experimentation to drive innovation.
In this regard, Levänen et al. (2022) report that the sustainability outcomes of Jugaad innovations often depend more on their business models than their technological innovation.
Open Innovation
Open innovation involves collaborating with external partners, including customers, suppliers, and even competitors, to co-create innovative solutions. This approach can help companies leverage external expertise and resources to drive Jugaad innovation.
Fischer et al. (2021) describe the effectiveness of university-industry collaboration partnerships in developing frugal innovations in emerging economies; they recommend that policymakers should promote social programs that enhance the active involvement of all actors in the business and innovation ecosystem.
Examples of Frugal Innovation
The health crisis triggered by COVID-19 became a driver for frugal innovation. Here are two examples that embody the frugal approach:
Face Shields
During the COVID-19 pandemic, a group of over 17,000 Spanish citizens with 3D printers in their homes formed the Coronavirus Makers and produced face shields for public health and citizens, reducing the selling price from EUR30 to EUR3.0 (Delfa, 2020).
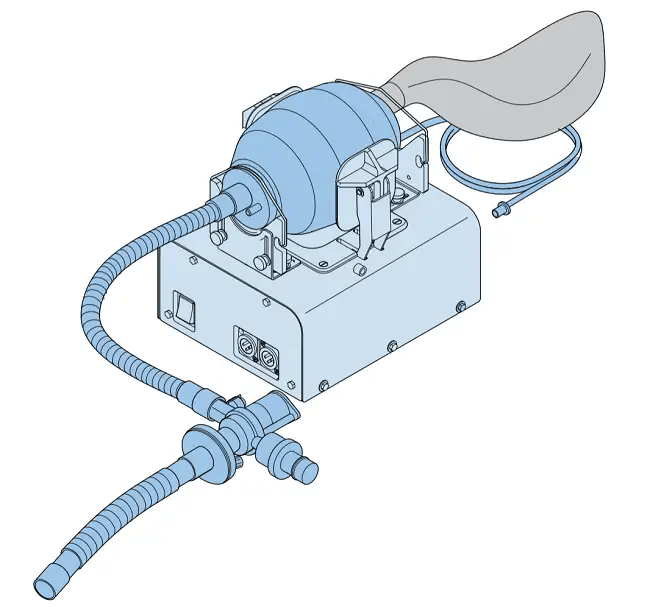
Respiratory Ventilator
In the Netherlands, researchers developed the open-source VentilatorPAL respiratory ventilator, which costs a fraction of a conventional respirator and is certified.
VentilatorPAL offers a solution to the acute shortage of ventilators for COVID-19 patients worldwide. Interested parties can access files on the Free Breathing website and have the option to build their own ventilators.
M-Pesa by Safaricom
M-Pesa, a mobile money transfer service launched by Safaricom in Kenya, revolutionized how people in rural areas access financial services. Leveraging existing mobile infrastructure, M-Pesa made it possible for people to send and receive money using their mobile phones, even without a bank account.
Grameen Bank
Grameen Bank, founded by Muhammad Yunus, pioneered the concept of microfinance, providing small loans to entrepreneurs in rural areas of Bangladesh. This Jugaad innovation helped lift millions out of poverty and created sustainable businesses in the process.
GE Healthcare
GE Healthcare developed the MAC 400, a portable electrocardiogram (ECG) machine designed specifically for rural areas in developing countries. By simplifying the design and reducing costs, GE Healthcare was able to provide affordable healthcare solutions to underserved communities.
Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble launched the ‘Shiksha‘ campaign in India, aimed at providing education to underprivileged children. Instead of relying on traditional advertising methods, Procter & Gamble used low-cost media channels and leveraged partnerships with local NGOs to raise awareness and funds for the cause.
Aravind Eye Care System
The Aravind Eye Care System in India revolutionized the delivery of eye care services by implementing a high-volume, low-cost model. By optimizing processes, leveraging economies of scale, and using innovative surgical techniques, the Aravind Eye Care System was able to provide quality eye care services to millions at affordable prices.
Challenges and Limitations of Frugal Innovation
While frugal innovation offers many advantages, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. Some of these include:
- Limited Resources: Jugaad innovation requires companies to work with limited resources and constraints. While this can foster creativity, it can also restrict the scope of innovation and make scaling operations more difficult.
- Quality Concerns: Balancing affordability with quality can be a challenge in Jugaad innovation. Companies must ensure that their products and services meet required standards and customer expectations while keeping costs low.
- Cultural Barriers: Jugaad innovation often involves thinking outside the box and challenging established norms. This can encounter resistance in some organizational cultures, making it challenging to implement frugal innovation initiatives.
- Market Acceptance: Jugaad innovation may face challenges in gaining market acceptance, especially in markets where customers are accustomed to high-quality, high-priced products. Convincing customers of the value and quality of frugal innovations can be a hurdle for companies.
Despite these challenges, companies that can overcome them can reap the numerous benefits that frugal innovation offers.
Conclusion
Frugal innovation becomes a viable alternative for ‘producing more with fewer resources.‘ This type of innovation can help you generate a new product for new customers.
Frugality is revolutionizing how businesses operate, enabling them to achieve more with less and drive success in the competitive current market. By embracing the principles of simplicity, affordability, sustainability, and flexibility, companies can create innovative solutions that are accessible to a broader customer base.
While Jugaad innovation comes with its challenges and limitations, the benefits are undeniable. From cost savings and market expansion to increased competitiveness and environmental sustainability, frugal innovation offers numerous advantages for companies of all sizes and industries.
So, if you’re looking to revolutionize your business and thrive in today’s fast-paced world, it’s time to embrace frugal innovation. Adopt the mindset of doing more with less, challenge conventional thinking, and leverage limited resources as opportunities for creativity. By thinking frugally and implementing innovative solutions, you can unlock the full potential of Jugaad innovation and achieve significant results for your business.
Bibliographic References
Albert, M. (2022). Assessing the sustainability impacts of frugal innovation–A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 365, 132754.
Corsini, L., Dammicco, V. and Moultrie, J. (2021), Frugal innovation in a crisis: the digital fabrication maker response to COVID-19. R&D Management, 51: 195-210. https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12446
Dabić, M., Obradović, T., Vlačić, B., Sahasranamam, S., & Paul, J. (2022). Frugal innovations: A multidisciplinary review & agenda for future research. Journal of Business Research, 142, 914-929.
Delfa B. 2020. Innovación frugal: más con menos para un mundo mejor. The Conversation.
Fischer, B., Guerrero, M., Guimón, J. and Schaeffer, P.R. (2021), “Knowledge transfer for frugal innovation: where do entrepreneurial universities stand?“, Journal of Knowledge Management, Vol. 25 No. 2, pp. 360-379. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-01-2020-0040
Gupta A. and H. Wang. 2009. Getting China and India Right: Strategies for Leveraging the World’s Fastest-Growing Economies for Global Advantage. Wiley.
Hossain M. 2020. Frugal innovation: Conception, development, diffusion, and outcome. Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 262, 2020, 121456, ISSN 0959-6526,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121456.
Khan, Rakhshanda. 2016. “How Frugal Innovation Promotes Social Sustainability” Sustainability 8, no. 10: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8101034
KOERICH, GRAZIELE VENTURA, & CANCELLIER, ÉVERTON LUÍS PELLIZZARO DE LORENZI. (2019). Frugal Innovation: origins, evolution and future perspectives. Cadernos EBAPE.BR, 17(4), 1079-1093. Epub January 20, 2020.https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-395174424x
Levänen, J., Hossain, M., & Wierenga, M. (2022). Frugal innovation in the midst of societal and operational pressures. Journal of Cleaner Production, 347, 131308.
Merriam-Webster. (2016). Frugal. En Diccionario online Merriam-Webster. (11e ed.).
Prathap, G. 2014. The myth of frugal innovation in India. Current Science, 106(3), 374-377.
Prabhu J. 2017. Frugal innovation: doing more with less for more. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 375: 20160372. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2016.0372
Radjou N., J. Prabhu, S. Ahuja. 2012. Jugaad Innovation: Think Frugal, Be Flexible, Generate Breakthrough Growth.
Radjou N. and J. Prabhu. 2013. Frugal Innovation: A New Business Paradigm. INSEAD Knowledge.
Weyrauch T. and C. Herstatt. 2016. What is frugal innovation? Three defining criteria. Weyrauch and Herstatt Journal of Frugal Innovation (2016) 2:1
DOI 10.1186/s40669-016-0005-y