In today’s fast-paced digital world, education has undergone a profound transformation. The term “Education 4.0” is on everyone’s lips, but what does it mean and how is it shaping the future of learning?
To succeed in their studies, life, and work, students must master 21st-century skills such as creativity and critical thinking, as well as socio-emotional learning traits like curiosity and resilience (Akimov et al., 2023). All of this is framed within the context of new digital technologies that are shaping the industry.
Education 4.0 is a response to the needs of Industry 4.0, where humans and technology align to enable new possibilities (Hussin, 2018), but above all to overcome challenges such as the lack of digital culture, training, knowledge, and language faced by Industry 4.0 in implementing its operations (Hariharasudan and Kot, 2018).
Whether you are an educator, a student, or simply wish to learn more about this topic, this article will unravel the mysteries of Education 4.0 and provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this educational paradigm shift.
What is Education 4.0?
To embark on this journey, it is essential to begin by understanding the central concept of Education 4.0. This educational revolution is closely tied to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, an era characterized by the integration of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and automation into various aspects of our lives. Education 4.0, therefore, signifies a corresponding transformation in the way we learn, teach, and prepare for the future.
Hariharasudan and Kot (2018) emphasize that Education 4.0 aims to enhance digital technological competencies at all levels and improve the use of digital technologies for teaching and learning. The focus works in three ways: basic digital education for all students and educators, digitally competent students and employees, and digital educational resources.
Meanwhile, Miranda et al. (2021) define Education 4.0 as the “current period in which higher education institutions apply new learning methods, innovative teaching and management tools, and intelligent and sustainable infrastructure, primarily complemented with new and emerging ICT to enhance knowledge generation and information transfer processes“.
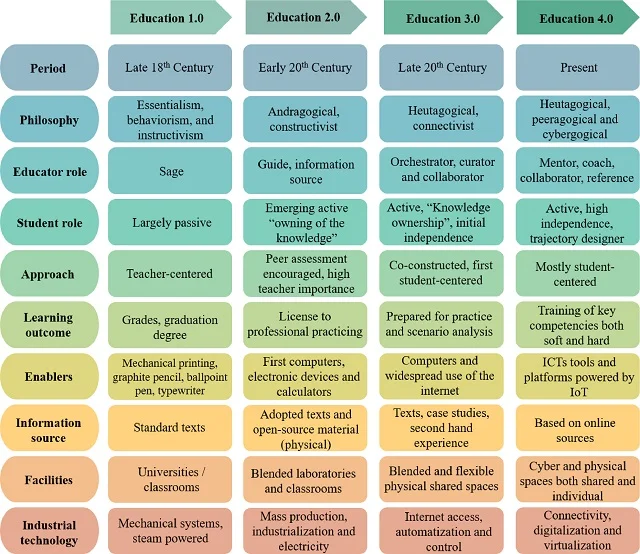
Education 4.0 Approach
Education 4.0 is a pedagogical approach aligned with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Caballero-Morales et al., 2020 and Costan et al., 2021), incorporating a dynamic, personalized, and technology-savvy learning approach. It leverages the power of technology to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in a constantly changing world.
According to the research findings of Himmetoglu et al. (2020), open access, individualized education, mindset transformation, integration of digital technologies into education, learning environments, lifelong learning, exploratory education, and multidisciplinary education are the key components that define Education 4.0.
Huk (2022), on the other hand, emphasizes that Education 4.0 is a concept aimed at ensuring sustainable development by integrating social, cultural, and educational activities in the digital medium. Meanwhile, Caballero-Morales et al. (2020) consider, on one hand, the exploitation of technologies developed to facilitate the teaching process and, on the other hand, the methods and workshops that will familiarize aspiring engineers with these technologies already operating in Industry 4.0 environments.
Traditional classrooms are giving way to digital platforms, and teachers are evolving into facilitators of learning experiences. In this regard, Education 4.0 is based on the concept of learning by doing, encouraging students to learn and discover things in unique ways through experimentation (Almeida and Simoes, 2019).
The World Economic Forum published a white paper that defines a framework for Education 4.0 (Table 1), recommending content and experiences that should be implemented in educational models.
Table 01. The World Economic Forum’s Education 4.0 framework.
| Content (built-in mechanisms for skills adaptation) | Experiences (utilization of innovative pedagogies) |
| Global citizenship skills To include content that focuses on building awareness about the wider world, sustainability and playing an active role in the global community. | Personalized and self-paced learning From a system where learning is standardized, to one based on the diverse individual needs of each learner, and flexible enough to enable each learner to progress at their own pace. |
| Innovation and creativity skills To include content that fosters skills required for innovation, including complex problem solving, analytical thinking, creativity and system analysis. | Accessible and inclusive learning From a system where learning is confined to those with access to school buildings to one in which everyone has access. |
| Technology skills To include content that is based on developing digital skills, including programming, digital responsibility and the use of technology. | Problem-based and collaborative learning From process-based to project- and problem-based content delivery, requiring peer collaboration and more closely mirroring the future of work. |
| Interpersonal skills To include content that focuses on interpersonal emotional intelligence (i.e. empathy, cooperation, negotiation, leadership and social awareness). | Lifelong and student-driven learning From a system where learning and skilling decrease over one’s lifespan to one where everyone continuously improves on their existing skills and acquires new ones based on their individual needs. |
Trends in Education 4.0
In the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, our approach to education has undergone a remarkable evolution. This transformation, often referred to as Education 4.0, is reshaping the landscape of learning and teaching. In this regard, Miranda et al. (2021) report that pedagogical approaches are also evolving and realigning their paradigms towards innovation in their instructional processes to meet the needs of a technologically evolving society.
As we delve into the heart of this educational revolution, it is imperative to understand the key trends shaping the future of Education 4.0.
Personalized Learning
Personalization has become the cornerstone of Education 4.0. With the help of advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence, educators can tailor learning experiences to meet the unique needs and preferences of each student. Students are no longer confined to a one-size-fits-all model; instead, they embark on a personalized learning journey that adapts to their pace and learning style.
This trend not only enhances engagement and motivation but also leads to more effective knowledge acquisition. Personalized learning is breaking down traditional barriers in education, allowing students to thrive at their own pace.
Blended Learning
Blended learning is a hybrid approach that combines traditional classroom instruction with digital technology. In Education 4.0, educators employ a rich variety of digital tools and resources, including online lectures, interactive modules, and collaborative platforms. This fusion of physical and digital realms offers flexibility and adaptability, ensuring that students receive a comprehensive education.
Blended learning is particularly beneficial in bridging the gap between traditional and online education. It facilitates a dynamic learning environment that caters to diverse learning styles, making education more accessible and effective.
Lifelong Learning
Education is no longer limited to a specific age or stage of life. The concept of lifelong learning is at the core of Education 4.0. In this era, individuals are encouraged to continuously acquire new skills and knowledge throughout their lives. This is not only crucial for personal growth but also for remaining competitive in a rapidly changing job market.
Lifelong learning is facilitated by a multitude of resources, courses, and online platforms, making it easier than ever to improve skills or pivot in one’s career. Education is a lifelong journey, and Education 4.0 ensures that this journey is not restricted by traditional limitations.
Online Education Platforms
The rise of online education platforms has been a defining feature of Education 4.0. These platforms have democratized education, making it accessible to students worldwide. Whether through Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) or dedicated e-learning platforms, students can now access high-quality educational content from the comfort of their homes.
Online education offers convenience, flexibility, and affordability, making it a popular choice for those looking to advance their education without location or time constraints. It is a testament to the power of technology in breaking down educational barriers.
Competency-Based Learning
Competency-based learning departs from traditional education and focuses on mastering specific skills and knowledge rather than time spent in the classroom. This approach allows students to progress based on demonstrated skills and understanding, rather than adhering to a rigid academic schedule.
Competency-based education closely aligns with the needs of the job market, ensuring that students are well-prepared with practical skills and competencies. It empowers students to take ownership of their education and prepares them for success in a skill-driven world.
Gamification and Immersive Learning
Engagement is a key factor in Education 4.0, and gamification and immersive learning experiences play a significant role in achieving it. Gamification elements such as badges, points, and challenges motivate students and enhance their learning experiences.
Additionally, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being employed to create immersive learning environments. These technologies allow students to explore subjects in a practical and interactive manner, from dissecting virtual frogs in biology to exploring ancient civilizations in history.
Barriers to Implementing Education 4.0
The implementation of the Education 4.0 approach represents a challenge for traditional educational systems. In this context, educational administrators must identify the barriers they will face in adapting to the demands of the 21st century.
Costan et al. (2021) identified 12 barriers to the implementation of Education 4.0: Cybersecurity threats, Costs, Human capital capability gaps, Apprehensive stakeholders, Lack of resources for training, Lack of collaboration, Knowledge gap for curriculum design personalization, Insufficient available technologies, Health issues, Time constraints for material preparation, Complexity of learning platforms, and Insufficient foundation in basic education.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Education 4.0
Education 4.0 is intrinsically linked to the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). This industrial revolution is characterized by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and more. To adapt to this new reality, education must prepare students for the jobs and challenges of the future.
In this regard, González-Pérez and Ramírez-Montoya (2022) highlight that incorporating Industry 4.0 technologies into education requires updating educational systems, starting with classroom organization and management, assessment, pedagogy, ethics, and professional development. They conclude that educational models should integrate artificial intelligence, data management, ubiquitous technologies, robots, and cloud computing.
Education 4.0 emphasizes the development of skills such as critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and adaptability. These skills are essential in a world where routine tasks are increasingly automated, and the workforce must continuously evolve to remain competitive.
Examples of Education 4.0
The research findings of Moraes et al. (2023) show that increased use of augmented reality, simulation, the Internet of Things, and virtual reality is more prevalent at higher education levels.
Let’s explore some real-world examples of Education 4.0 in action:
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: Platforms like Khan Academy and Duolingo use algorithms to personalize the learning journey, adapting content based on the student’s progress.
- Virtual Reality in Education: VR technology is used to create immersive learning experiences. For example, medical students can practice surgery in a virtual environment before entering the operating room.
- Coding Bootcamps: Intensive coding bootcamps offer condensed, job-focused education that equips participants with on-demand programming skills.
- Microlearning: Short, easily digestible content, often delivered through mobile apps, allows students to acquire knowledge in short, focused periods.
Conclusion
Education 4.0 represents a paradigm shift in the world of learning. It is an educational system that leverages technology to create personalized, adaptable, and lifelong learning experiences. Its goal is to prepare individuals for the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In conclusion, the trends in Education 4.0 are redefining the way we approach learning and teaching. This evolution extends beyond the classroom to lifelong learning, personalized experiences, and technology integration. By embracing these trends, we pave the way for a more adaptable, inclusive, and effective educational system that equips students with the skills they need to succeed in the Fourth Industrial Revolution and beyond.
This article has only scratched the surface of Education 4.0. The journey to understanding this transformative concept is just beginning, but the possibilities are limitless. Stay curious and open to change because Education 4.0 is an exciting frontier that holds the key to unlocking the potential of future generations. As the digital age advances, one thing is clear: Education 4.0 is the way forward.
Bibliographical References
Akimov, N., Kurmanov, N., Uskelenova, A., Aidargaliyeva, N., Mukhiyayeva, D., Rakhimova, S., … & Utegenova, Z. (2023). Components of education 4.0 in open innovation competence frameworks: systematic review. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 100037.
Almeida, F., & Simoes, J. (2019). The role of serious games, gamification and industry 4.0 tools in the education 4.0 paradigm. Contemporary Educational Technology, 10(2), 120-136.
Caballero-Morales, S.-O., Cordero Guridi, J. de J., Alvarez-Tamayo, R. I., & Cuautle-Gutiérrez, L. (2020). EDUCATION 4.0 TO SUPPORT ENTREPRENEURSHIP, SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT AND EDUCATION IN EMERGING ECONOMIES. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 8(2), 89–100. https://doi.org/10.37335/ijek.v8i2.119
Costan, E.; Gonzales, G.; Gonzales, R.; Enriquez, L.; Costan, F.; Suladay, D.; Atibing, N.M.; Aro, J.L.; Evangelista, S.S.; Maturan, F.; et al. Education 4.0 in Developing Economies: A Systematic Literature Review of Implementation Barriers and Future Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212763
González-Pérez, L.I.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.S. Components of Education 4.0 in 21st Century Skills Frameworks: Systematic Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031493
Hariharasudan, A.; Kot, S. A Scoping Review on Digital English and Education 4.0 for Industry 4.0. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci7110227
Himmetoglu, B., Aydug, D., & Bayrak, C. (2020). Education 4.0: Defining the teacher, the student, and the school manager aspects of the revolution. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 21(Special Issue-IODL), 12-28.
Huk, T. (2021). From education 1.0 to education 4.0-challenges for the contemporary school. The New Educational Review, 66, 36-46.
Hussin, A. A. (2018). Education 4.0 made simple: Ideas for teaching. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 6(3), 92-98.
Miranda, J., Navarrete, C., Noguez, J., Molina-Espinosa, J. M., Ramírez-Montoya, M. S., Navarro-Tuch, S. A., … & Molina, A. (2021). The core components of education 4.0 in higher education: Three case studies in engineering education. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 93, 107278.
Moraes, E.B., Kipper, L.M., Hackenhaar Kellermann, A.C., Austria, L., Leivas, P., Moraes, J.A.R. and Witczak, M. (2023), “Integration of Industry 4.0 technologies with Education 4.0: advantages for improvements in learning“, Interactive Technology and Smart Education, Vol. 20 No. 2, pp. 271-287. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-11-2021-0201
WEF. 2023. Defining Education 4.0: A Taxonomy for the Future of Learning. 28 p.