Imagine a future where doctors spend less time on paperwork and more time with patients. A recent study suggests that this future might be closer than we think, thanks to advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The AI model ChatGPT can write administrative medical notes up to ten times faster than doctors without compromising quality. This is according to a new study conducted by researchers from Uppsala University Hospital and Uppsala University in collaboration with Danderyd Hospital and the University Hospital of Basel.
The paperwork burden
Doctors devote a significant amount of time to administrative tasks, including writing discharge summaries. This can take away valuable time from patient interaction.
“For years, the debate has focused on how to improve healthcare efficiency. Thanks to advances in generative AI and language modeling, there are now opportunities to reduce the administrative burden on healthcare professionals. This will allow doctors to spend more time with their patients,” explains Cyrus Brodén, orthopedic surgeon and researcher at Uppsala University Hospital and Uppsala University.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models like ChatGPT-4 are computer programs trained on massive amounts of text data. This enables them to generate human-quality writings, potentially including medical documents.
The study: Can AI write accurate discharge notes?
The study aimed to assess the quality and effectiveness of the ChatGPT tool in producing clinical history notes.
Researchers investigated whether ChatGPT-4 could produce accurate and efficient discharge summaries for orthopedic patients. They conducted a pilot study of just six cases of virtual patients, which will now be followed by an in-depth study of 1,000 authentic patient medical records.
The process
Researchers used six cases of virtual patients mimicking real cases in both structure and content. Orthopedic physicians generated discharge documents for each case.
- Creation of realistic scenarios: Physicians created detailed medical records for six fictional orthopedic cases.
- Human vs. machine: Both junior doctors and an advanced resident physician wrote discharge summaries for each case. ChatGPT-4 was then asked to create summaries using the same information.
- Quality control: A panel of medical experts judged the quality of all discharge summaries, unaware of whether humans or AI wrote them.
- Speed test: Researchers also tracked how long it took doctors and ChatGPT-4 to complete the summaries.
The results
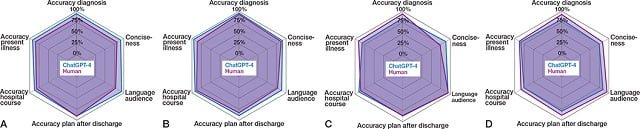
Quality parity: The key finding? ChatGPT-4’s discharge summaries were comparable in quality to those written by doctors. This is promising news for the potential use of AI in creating medical documents.
- Speed advantage: However, the most impressive result was speed. ChatGPT-4 generated discharge summaries surprisingly 10 times faster than human doctors!
- A note on accuracy: There were some cases where ChatGPT-4 included inaccurate information, but interestingly, this occurred less frequently than errors found in summaries written by humans.
“The results show that ChatGPT-4 and human-generated notes are comparable in overall quality, but ChatGPT-4 produced discharge documents ten times faster than doctors,” notes Brodén.
“Our interpretation is that advanced large language models like ChatGPT-4 have the potential to change the way we handle administrative tasks in healthcare. I believe generative AI will have a significant impact on healthcare, and this could be the beginning of a very interesting development,” he maintains.
What this means for the future of healthcare
The plan is to launch an in-depth study soon, where researchers will gather 1,000 patient medical records. Again, the goal is to use ChatGPT to produce similar administrative notes in patient records.
“It will be an interesting project that will require a lot of resources and involve many partners. We are already actively working to meet all confidentiality and data management requirements to launch the study,” Brodén concludes.
The study highlights the potential of AI to significantly reduce administrative burdens on healthcare professionals. Faster discharge summaries mean doctors can spend more time with patients, improving overall healthcare efficiency.
It’s important to note: AI is still in development in healthcare settings and more research is needed. But this study suggests a bright future where AI can help doctors focus on what matters most: their patients.
Reference (open access)
Rosenberg, G. S., Magnéli, M., Barle, N., Kontakis, M. G., Müller, A. M., Wittauer, M., Gordon, M., & Brodén, C. (2024). ChatGPT-4 generates orthopedic discharge documents faster than humans maintaining comparable quality: a pilot study of 6 cases. Acta Orthopaedica, 95, 152–156. https://doi.org/10.2340/17453674.2024.40182