While many companies are driving the digitization of their processes to interconnect new technologies to improve efficiency and productivity (Industry 4.0), the next phase of industrialization is already among us.
Industry 5.0, also known as the Fifth Industrial Revolution, is the next generation of manufacturing technology that will change the way products are designed, built, and delivered. This new era of smart factories will create an entirely new industrial ecosystem where machines, sensors, software, and people collaborate to produce goods in real time, primarily focused on sustainability.
The Fifth Industrial Revolution will become part of the daily business due to the speed of technological development and the evolving integration of human processes. We will witness an explosion of new technologies that will help us do things faster, better, and more cost-effectively than ever before.
In this article, we want to provide you with a fairly general overview of Industry 5.0, presenting different definitions, characteristics, examples, and a comparison with Industry 4.0.
What is Industry 5.0?
The Fifth Industrial Revolution is the combination of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, artificial intelligence, and human creativity, which will transform the way businesses operate. These technologies will work together to make our lives easier, more efficient, and safer, to place human well-being at the center of manufacturing systems, achieve social goals beyond employment and growth to provide solid prosperity for the sustainable development of humanity as a whole (Leng et al., 2022).
Müller (2020) and Xun et al. (2021) report that the European Commission emphasizes that Industry 5.0 recognizes the power of the industry to achieve social goals beyond employment and growth, to become a resilient provider of prosperity, ensuring that production respects the limits of our planet and placing the well-being of industry workers at the center of the production process.
According to the European Commission, Industry 5.0 places worker well-being at the center of the production process and uses new technologies to provide prosperity beyond employment and growth while respecting the productive limits of the planet. It emphasizes that Industry 5.0 “offers a vision of the industry that goes beyond efficiency and productivity as the sole objectives and reinforces the role and contribution of the industry to society.”
Alpaslan et al. (2019) report that two visions emerged from the Fifth Industrial Revolution. The first is “human-robot co-work,” where robots and humans work together, with humans focusing on tasks requiring creativity while robots handle the rest. The other vision for Industry 5.0 is bioeconomics.
However, it’s important to note that the goal of Fifth Industrial Revolution is to leverage the creativity of human experts in collaboration with efficient, intelligent, and precise machines to achieve resource-efficient manufacturing solutions preferred by users (Praveen et al., 2022). Industry 5.0 goes beyond this; Leng et al. (2022) highlight that the Fifth Industrial Revolution places human well-being at the center of manufacturing systems, achieving social goals beyond employment and growth to provide solid prosperity for the sustainable development of humanity.
In this sense, Industry 5.0 represents the introduction of a new paradigm that eliminates the separation between humans and technology (Orea et al., 2022); according to the European Commission (2022), it is based on three key pillars: human-centered, resilient, and sustainable.
Characteristics of Industry 5.0
The Fifth Industrial Revolution builds on Industry 4.0 technologies; however, it goes beyond by emphasizing the potential of human creativity to create a new “human-machine” collaborative working approach. Kraaijenbrink (2022) reports that the applicability of Industry 5.0 is significantly broader than that of Industry 4.0.
Praveen et al. (2022) describe that Industry 5.0 is based on technologies such as edge computing, digital twins, collaborative robots, the Internet of Everything, blockchain, and 6G networks. However, Ivanov (2022) adds that Industry 5.0 is a combination of organizational principles and technologies to design and manage operations and supply chains as resilient, sustainable, and human-centered systems.
It’s also important to highlight that the Fifth Industrial Revolution uses predictive analytics and operational intelligence to create models aimed at making more precise and less volatile decisions. It enhances the end customer experience by applying various tools, considering artificial intelligence and robotics (Orea et al., 2022). In this regard, Nahavandi (2019) anticipates that the Fifth Industrial Revolution will create a new manufacturing role: Chief Robotics Officer (CRO); according to the researcher, a CRO is a person with expertise in knowledge of robots and their interactions with humans.
In an Industry 5.0 work environment, robots can perceive, understand, and sense the human operator, as well as the goals and expectations of the tasks being performed (Akundi et al., 2022).
Finally, Praveen et al. (2022) report that mass customization is another significant contribution of Industry 5.0, where customers can prefer personalized products tailored to their tastes and needs.
Core Values of Industry 5.0
Xun et al. (2021) report that Industry 5.0 focuses on three interconnected core values: human-centered, sustainability, and resilience.

Human-Centered
Places fundamental human needs and interests at the center of the production process, shifting from technology-driven progress to a fully human and society-centered approach.
A safe and inclusive working environment should be created to prioritize physical health, mental health, and overall well-being, ultimately safeguarding the fundamental rights of workers, such as autonomy, human dignity, and privacy.
Join the Community
Get the best ideas, analysis, and trends on innovation delivered straight to your inbox. No spam, just value!
Sustainability
For the industry to respect planetary limits, it needs to develop circular processes that reduce, reuse, and recycle natural resources, decrease waste and environmental impact, ultimately leading to a circular economy with better resource efficiency and effectiveness.
Resilience
Refers to the need to develop a higher degree of robustness in industrial production, better arming it against disruptions, and ensuring it can provide and support critical infrastructure in times of crisis.
Dimensions of Industry 5.0
Ivanov (2022) identified that Industry 5.0 has four main dimensions:
- Key technological principles of Industry 5.0 are collaboration, coordination, communication, automation, data analytics processing, and identification.
- Fifth Industrial Revolution covers four areas: organization, management, technology, and performance assessment.
- Industry 5.0 encompasses three levels: societal level, network level, and plant level.
- Industry 5.0 frames a new triple outcome of resilient value creation, human well-being, and sustainable society.
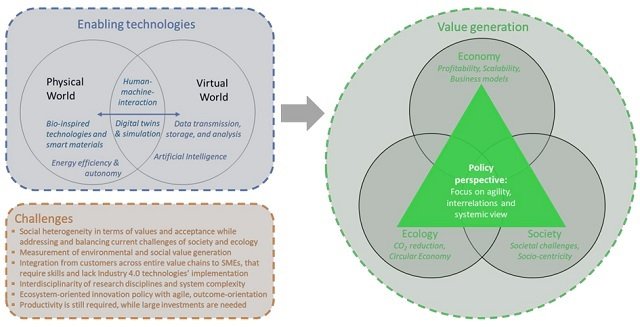
Technologies of Industry 5.0
Müller (2020) and Maddikunta et al. (2022) describe the technologies underpinning the concept of the Fifth Industrial Revolution, including edge computing, digital twins, collaborative robots, the Internet of Things, blockchain, 6G networks, and beyond.
Here’s a brief description of each technology:
- Human-centered solutions and human-machine interaction technologies that interconnect and combine the skills of humans and machines.
- Bio-inspired technologies and smart materials enabling materials with built-in sensors and enhanced features while being recyclable.
- Real-time-based digital twins and simulation to model complete systems.
- Cybersecure data transmission, storage, and analysis technologies capable of handling data and system interoperability.
- Artificial intelligence to detect causality in complex and dynamic systems, leading to actionable intelligence. AI is used in manufacturing to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and customize production.
- Internet of Things is used in manufacturing to collect data from machines and processes, which can be used to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Technologies for energy efficiency and reliable autonomy, as the mentioned technologies will require large amounts of energy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Industry 5.0
The emergence of concepts like Industry 5.0 presents new opportunities and challenges for businesses (Aslam et al., 2020). Innovations of the Fifth Industrial Revolution will make our lives easier, safer, and more efficient, improving the quality of life for everyone.
According to Nahavandi (2019), the Fifth Industrial Revolution will bring unprecedented challenges in the field of human-machine interaction (HMI) as it will bring machines very close to the everyday life of any human being.
Industry 5.0 will revolutionize manufacturing systems worldwide by eliminating boring, dirty, and repetitive tasks from human workers whenever possible (Nahavandi, 2019; Javaid Mohd and Haleem, 2020). In this sense, we can list the following benefits of Fifth Industrial Revolution:
- Increased Efficiency: Industry 5.0 can help manufacturers automate tasks, improve decision-making, and customize production. This can lead to significant improvements in efficiency.
- Higher Productivity: The Fifth Industrial Revolution can help manufacturers produce more products with fewer resources. This can lead to higher productivity and profitability.
- Reduced Costs: Industry 5.0 can help manufacturers reduce costs by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing waste.
- Improved Quality: The Fifth Industrial Revolution can help manufacturers improve quality by automating tasks, collecting data, and using AI to identify and correct issues.
- Greater Sustainability: Industry 5.0 can help manufacturers reduce their environmental impact by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and using renewable energy.
Among the main disadvantages of the Fifth Industrial Revolution is the lack of standards and legal norms to prevent problems between technology, society, and businesses. Also, consideration must be given to how autonomous systems can incorporate ethical principles (Nahavandi, 2019).
Moreover, Adel (2022) describes that the challenges of Industry 5.0 include security, privacy, a lack of skilled workers, slow processes, and the large budget required.
Industry 5.0 vs Industry 4.0
The main goal of Industry 4.0 is to make manufacturing “smart” by interconnecting machines; the main priority is the automation process, consequently reducing human intervention in manufacturing processes. In contrast, Industry 5.0 focuses on the worker. In this regard, Ghobakhloo et al. (2022) developed a model for the fifth industrial revolution showing that Industry 5.0 is a sociotechnological phenomenon that depends on technological advances and stakeholder collaboration to go beyond economic development and address prevailing environmental and social concerns.
Hein-Pensel et al. (2023) offer a clearer differentiation, stating that “while Industry 4.0 still primarily focuses on economic goals that must be achieved through digital transformation and the automation of monotonous work processes, Industry 5.0 will also bring social and ecological goals.”
According to the European Commission, Industry 5.0 complements the existing approach of “Industry 4.0” by specifically placing research and innovation in the service of the transition towards a sustainable, human-centered, and resilient industry. In Table 01, you can find a comparison between both industries.
Table 01. Comparison between Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0.
| Industry 4.0 | Industry 5.0 |
|---|---|
| Focuses on improving mass productivity and performance through the provision of intelligence between devices and applications using machine learning. | Seeks to leverage human creativity to collaborate with powerful, intelligent, and precise machinery. |
| Robots actively participate in large-scale production. | Focuses on massive customization, where humans guide robots. |
| Centers on the connectivity Cyber Physical Systems (CPS). | Links with Industry 4.0 applications and establishes a relationship between collaborative robots (cobots). |
| Driven by technology. | Driven by value. |
| Mass production | Smart society and sustainability |
| Technologies involved: Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, Big Data, Robotics, and Artificial Intelligence. | Technologies involved: Human-robot collaboration, bionics |
| Research areas: Organizational research, process improvement, and innovation. | Research areas: Smart environments, organizational research, process improvement, and innovation. |
Examples of Industry 5.0
The evolution of the Fifth Industrial Revolution is present in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and other industries (Adel, 2022). Praveen et al (2022) describe possible applications of Industry 5.0, such as smart healthcare, cloud manufacturing, supply chain management, and manufacturing production.
Perhaps the most well-known application of Fifth Industrial Revolution is in manufacturing, where it is considered a new production model that focuses on the interaction between humans and machines (Adel, 2022).
Qathan et al. (2022) highlights the use of electric vehicles as a mode of transportation in the Fifth Industrial Revolution; consequently, significant efforts are being made to integrate sustainable transport modeling approaches to support the electric passenger vehicle industry.
Adel (2022) reports that the Fifth Industrial Revolution will enable the creation of a real-time smart hospital, while Iyengar et al. (2022) indicate that the evolution of Industry 5.0 paves the way to introduce personalized products in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of a spectrum of orthopedic pathologies, allowing the design of tools, instruments, and implants specific to patients.
Challenges of Industry 5.0
While Industry 5.0 has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing, it also faces a series of challenges, including:
- Need for skilled workers: The Fifth Industrial Revolution requires workers with new skills and knowledge. Manufacturers will need to invest in training and education to ensure they have the workforce needed to adopt Industry 5.0.
- Data and system security: Industry 5.0 relies on the use of connected data and systems. Manufacturers will need to invest in security to protect their data and systems from cyberattacks.
- Ethical implications of artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence raises a series of ethical concerns, such as the potential for bias and discrimination. Manufacturers will need to be aware of these concerns and develop ethical guidelines for the use of AI in manufacturing.
Conclusions
Industry 5.0 is still in its early stages but has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing. By adopting these new technologies, manufacturers can create more efficient, productive, and sustainable operations.
According to Nahavandi (2019), as a direct impact of Industry 5.0, a large number of startups will create a new ecosystem to provide personalized robotic solutions, both in terms of hardware and software, worldwide.
The Fifth Industrial Revolution places human well-being as an important part of the production process, both in terms of employment and end-users. In this regard, Industry 5.0 comes with the promise of a more responsible and resilient industry.
Even though Industry 5.0 has some advantages for fostering innovation and competitiveness, the cost of its implementation represents a serious limitation that will contribute to widening the gap between companies in developing and developed countries.
References
Adel, A. Future of industry 5.0 in society: human-centric solutions, challenges and prospective research areas. J Cloud Comp 11, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13677-022-00314-5
Akundi, Aditya, Daniel Euresti, Sergio Luna, Wilma Ankobiah, Amit Lopes, and Immanuel Edinbarough. 2022. “State of Industry 5.0—Analysis and Identification of Current Research Trends” Applied System Innovation 5, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi5010027
Alpaslan Demir Kadir, Gözde Döven, Bülent Sezen. 2019. Industry 5.0 and Human-Robot Co-working. Procedia Computer Science, Volume 158, 2019, Pages 688-695, ISSN 1877-0509, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.104.
Aslam, Farhan, Wang Aimin, Mingze Li, and Khaliq Ur Rehman. 2020. “Innovation in the Era of IoT and Industry 5.0: Absolute Innovation Management (AIM) Framework” Information 11, no. 2: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11020124
European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, Industry 5.0 roundtable : Brussels 27 April 2022 : meeting report, Publications Office of the European Union, 2022,
European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, Industry 5.0 – Human-centric, sustainable and resilient, Publications Office, 2020,
Ghobakhloo, M., Iranmanesh, M., Mubarak, M. F., Mubarik, M., Rejeb, A., & Nilashi, M. (2022). Identifying industry 5.0 contributions to sustainable development: A strategy roadmap for delivering sustainability values. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 33, 716-737.
Hein-Pensel, F., Winkler, H., Brückner, A., Wölke, M., Jabs, I., Mayan, I. J., … & Zinke-Wehlmann, C. (2023). Maturity assessment for Industry 5.0: A review of existing maturity models. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 66, 200-210.
Iyengar Karthikeyan P., Eindere Zaw Pe, Janaranjan Jalli, Madapura K. Shashidhara, Vijay K. Jain, Abhishek Vaish, Raju Vaishya. 2022. Industry 5.0 technology capabilities in Trauma and Orthopaedics. Journal of Orthopaedics, Volume 32, 2022, Pages 125-132, ISSN 0972-978X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2022.06.001.
Ivanov, D. (2023). The Industry 5.0 framework: Viability-based integration of the resilience, sustainability, and human-centricity perspectives. International Journal of Production Research, 61(5), 1683-1695.
Javaid Mohd and Abid Haleem. 2020. Critical Components of Industry 5.0 Towards a Successful Adoption in the Field of Manufacturing. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management 2020 05:03, 327-348
Kraaijenbrink Jeroen. 2022. What Is Industry 5.0 And How It Will Radically Change Your Business Strategy? Forbes.
Leng Jiewu, Weinan Sha, Baicun Wang, Pai Zheng, Cunbo Zhuang, Qiang Liu, Thorsten Wuest, Dimitris Mourtzis, Lihui Wang. 2022. Industry 5.0: Prospect and retrospect,
Journal of Manufacturing Systems, Volume 65, 2022, Pages 279-295, ISSN 0278-6125, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.09.017.
Maddikunta, P. K. R., Pham, Q. V., Prabadevi, B., Deepa, N., Dev, K., Gadekallu, T. R., … & Liyanage, M. (2022). Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 26, 100257.
Müller Julian. 2020. Enabling Technologies for Industry 5.0: Results of a workshop with Europe’s technology leaders. European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. 19 p.
Nahavandi, Saeid. 2019. “Industry 5.0—A Human-Centric Solution” Sustainability 11, no. 16: 4371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164371
Orea-Giner Alicia, Laura Fuentes-Moraleda, Teresa Villacé-Molinero, Ana Muñoz-Mazón, Jorge Calero-Sanz. 2022. Does the Implementation of Robots in Hotels Influence the Overall TripAdvisor Rating? A Text Mining Analysis from the Industry 5.0 Approach, Tourism Management, Volume 93, 2022, 104586, ISSN 0261-5177,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2022.104586.
Praveen Kumar Reddy Maddikunta, Quoc-Viet Pham, Prabadevi B, N Deepa, Kapal Dev, Thippa Reddy Gadekallu, Rukhsana Ruby, Madhusanka Liyanage. 2022. Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, Volume 26, 2022, 100257, ISSN 2452-414X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2021.100257.
Qahtan Sarah, H.A. Alsattar, A.A. Zaidan, Dragan Pamucar, Muhammet Deveci. 2022. Integrated sustainable transportation modelling approaches for electronic passenger vehicle in the context of industry 5.0. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, Volume 7, Issue 4, 2022, 100277, ISSN 2444-569X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2022.100277.
Xun Xu, Yuqian Lu, Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Lihui Wang. 2021. Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, Volume 61, 2021, Pages 530-535, ISSN 0278-6125, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.10.006.
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.