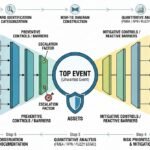
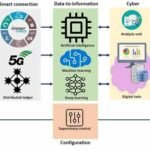
In today’s society, increasingly environmentally conscious, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword. It’s a way of life. At the forefront of this sustainability revolution is green manufacturing, also known as eco-friendly manufacturing or sustainable manufacturing. As industries strive to minimize their carbon footprint and reduce their impact on the planet, green manufacturing is redefining what it means to be sustainable.
This holistic approach aims to minimize resource consumption, waste generation, and pollutant emissions, driving a more sustainable future for the planet. Thus, the integration of sustainable strategies into manufacturing operations has become mandatory in recent years with the introduction of sustainable development goals (Kannan et al., 2022).
By focusing on the use of renewable energy, waste reduction, and resource minimization, green manufacturing is revolutionizing the industry. It’s no longer just about producing goods; it’s about producing them in a way that respects and preserves our planet for future generations.
By incorporating innovative technologies and processes, eco-friendly manufacturers can not only make their operations more environmentally friendly but also more profitable. These manufacturers understand that sustainability and profitability are not mutually exclusive. In fact, by adopting sustainable practices, they can increase efficiency, improve product quality, and attract a growing number of environmentally conscious consumers.
In this article, we will explore how green manufacturing is transforming industries worldwide and the key benefits it brings to companies, consumers, and the planet.
The importance of sustainability in the manufacturing industry
Sustainability has become a crucial factor in the manufacturing industry. The rapid depletion of natural resources and the growing threat of climate change have forced companies to rethink their operations and adopt sustainable practices. Sustainable manufacturing offers a solution by integrating environmentally friendly processes and technologies into production.
One of the key reasons sustainability is important in the manufacturing industry is the need to reduce the industry’s carbon footprint. Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on non-renewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
By transitioning to green manufacturing, companies can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and instead use renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power.
Additionally, sustainability in manufacturing goes beyond reducing carbon emissions. It also involves minimizing waste and optimizing resource consumption. Eco-friendly manufacturers implement strategies such as recycling, material reuse, and the adoption of lean manufacturing principles to ensure efficient resource use. These practices not only reduce costs but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the industry.
What is green manufacturing?
Green manufacturing, also known as eco-friendly manufacturing or sustainable manufacturing, is defined as a set of practices and strategies that integrate sustainability into all aspects of the production process. From material selection and energy efficiency to waste management and eco-compatible product design, green manufacturing seeks to minimize the environmental impact of the industry. Haleem et al., (2023) also indicate that “green manufacturing” is the term for innovative production methods aimed at reducing adverse environmental impacts through waste reduction, waste recycling, better utilization of natural resources, and other related measures.
On the other hand, Andaregie and Astatkie (2022) define Green Manufacturing Practices (GMP) as “unified and cost-effective methods used to reduce or eliminate all waste streams related to the design, manufacturing, and disposal of products and waste materials”.
In simple terms, sustainable manufacturing seeks to produce responsibly, minimizing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. This involves:
- Reducing energy and resource consumption such as water, materials, and raw materials.
- Minimizing waste generation and pollutant emissions.
- Using recycled and renewable materials.
- Implementing efficient and clean production practices.

Fundamental Principles of Green Manufacturing
The fundamental principles of sustainable manufacturing are based on resource consumption reduction, material reuse, and waste valorization. Additionally, it promotes energy efficiency, pollution prevention, and conservation of natural resources.
The principles underpinning green manufacturing are:
- Prevention: The best way to control pollution is to prevent it from the source.
- Eco-efficiency: Optimizing resource use and production to minimize environmental impact.
- Extended responsibility: Assuming product responsibility throughout its lifecycle.
- Design for the environment: Considering environmental impact from the product design phase.
- Cooperation: Collaboration between businesses, governments, and civil society to promote sustainability.
Eco-friendly Manufacturing Practices and Innovations
Eco-friendly manufacturing encompasses a wide range of practices and innovations aimed at minimizing environmental impact. These practices go beyond simple renewable energy use and include various strategies to reduce waste, conserve resources, and promote sustainable supply chains.
Energy Efficiency
One key practice in green manufacturing is energy efficiency. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies and processes to minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This includes the use of advanced equipment and systems designed to optimize energy use and eliminate energy waste.
Waste Reduction
Another important aspect of green manufacturing is waste reduction. Manufacturers are implementing strategies to minimize waste generation and maximize recycling and reuse. This includes implementing closed-loop systems, where waste materials are collected and reintroduced into the production process, reducing the need for raw materials and minimizing waste sent to landfills.
Adoption of Sustainable Practices
Additionally, eco-friendly manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This involves working closely with suppliers to ensure that raw materials are sourced responsibly and sustainably. It also includes promoting transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain to ensure ethical and environmentally friendly practices are followed.
The Sustainable Manufacturing Process
The green manufacturing process begins with the selection of sustainable raw materials and efficient production processes. The aim is to optimize energy and water use, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize waste generation.
The sustainable manufacturing process is based on the following stages:
- Assessment: Analysis of the company’s current environmental impact.
- Planning: Establishment of goals and strategies for environmental improvement.
- Implementation: Adoption of green manufacturing practices and technologies.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Tracking progress and measuring environmental impact.
- Continuous improvement: Implementation of measures to optimize environmental performance.
Monitoring Sustainable Manufacturing Indicators
Performance in sustainability is essential for companies to track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Fortunately, there are several tools and technologies available to help manufacturers assess their environmental impact and make data-driven decisions.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a widely used tool that quantifies the environmental impacts of a product or process throughout its lifecycle. LCA considers factors such as resource use, energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation. By conducting an LCA, manufacturers can identify critical points and prioritize actions to reduce their environmental footprint.
Another valuable technology is real-time monitoring systems, such as digital twins. These systems use sensors and data analytics to track energy use, emissions, and other relevant metrics in real-time. By continuously monitoring key indicators, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and implement corrective measures quickly.
Additionally, there are sustainability management software that provide a centralized platform for collecting, analyzing, and reporting sustainability data. These tools enable companies to optimize data management, generate reports, and compare their performance with industry standards.
Steps for Transitioning to Green Manufacturing
Transitioning to green manufacturing requires a systematic approach and careful planning. Here are the steps companies can take to embark on this journey towards sustainability:
- Evaluate current practices: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of current manufacturing processes, resource use, and waste generation. Identify areas where improvements can be made. A tool that can help you in this task is circular design.
- Set sustainability goals: Define clear and measurable sustainability goals that align with the company’s overall vision and values. These goals should cover areas such as energy efficiency, waste reduction, and supply chain sustainability.
- Research technologies and practices: Research and identify sustainable technologies and practices that are relevant to the business. Consider factors such as cost, feasibility, and potential impact on operations.
- Develop an implementation plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps, timeline, and resources needed to implement eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Assign responsibilities and establish key performance indicators to track progress.
- Engage stakeholders: Communicate the benefits of green manufacturing to employees, suppliers, and customers. Foster a culture of sustainability and involve stakeholders in the transition process. Additionally, cooperation with other companies through an industrial symbiosis approach can help achieve goals.
- Implement and monitor: Execute the implementation plan and continuously monitor performance. Periodically assess progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Celebrate achievements: Recognize and celebrate milestones and achievements along the path to sustainability. Share success stories to inspire others and reinforce commitment to green manufacturing.
It is important to note that the results of the research by Guo and Tsinopoulos (2023) revealed a positive association between environmental orientation, green manufacturing, organizational performance, and circular economy capability. Thus, the adoption of green manufacturing will have a significant impact throughout the company.
Benefits of Sustainable Manufacturing
The implementation of green manufacturing brings a series of benefits for companies, the environment, and society. Al-Hakimi et al. (2022) highlights that eco-friendly manufacturing has a positive indirect effect on companies’ sustainable performance through ecological innovation; while Haleem et al. (2023) emphasizes that green manufacturing can enhance environmental sustainability by adopting eco-technology and considering the complete product lifecycle, including research, production, use, and disposal.
Among them are:
- Cost reduction: Lower consumption of resources, energy, and water.
- Image enhancement: Greater social and environmental responsibility. Afum et al. (2020) highlights that green manufacturing has a significant positive impact on social, economic, and environmental performance.
- Increased competitiveness: Attraction of customers and partners committed to sustainability. D’Angelo et al. (2023) report that consumers are influenced by companies’ eco-friendly manufacturing practices in response to pressing environmental issues affecting our era.
- Compliance with regulations: Reduction of legal risks and fines.
- Contribution to sustainability: Environmental protection and combating climate change. Yan et al. (2022) describe that in the context of climate change, green manufacturing is a fundamental path to achieving a low-carbon economy.
Applications of Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Green manufacturing can be applied in a wide variety of industrial sectors. Saxena et al. (2022) published a scientific review on the application of green manufacturing across all industries, including transportation and electricity generation, cement industry, textile and garment industry, etc. Below are some examples of green manufacturing applications:
- Automotive: Manufacturing more efficient and lightweight vehicles.
- Electronics: Designing eco-compatible products and reducing planned obsolescence.
- Textile: Using recycled materials and sustainable production processes.
- Food: Reducing food waste and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Examples of Companies Implementing Green Manufacturing
Numerous companies have successfully implemented eco-friendly manufacturing practices and have reaped the benefits of sustainability. Let’s explore some case studies highlighting the transformative power of green manufacturing.
Tesla
Tesla, a pioneer in electric vehicles, is an excellent example of a company that has revolutionized the automotive industry through green manufacturing. By focusing on producing electric vehicles powered by renewable energy sources, Tesla has significantly reduced carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, Tesla’s Gigafactories, which produce batteries for their vehicles, operate on renewable energy, making the entire manufacturing process sustainable.
Patagonia
Patagonia, an outdoor clothing and gear company, has long been committed to sustainability. Its eco-friendly manufacturing initiatives include using recycled materials in its products, reducing water and energy consumption in its manufacturing processes, and promoting fair labor practices throughout its supply chain. These efforts have not only aligned Patagonia with environmentally conscious consumers but have also boosted its brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementing Green Manufacturing
While green manufacturing offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and barriers that companies may face when transitioning to sustainable practices. Kannan et al. (2022) highlight that green manufacturing acts as a basic platform for these extended manufacturing practices to promote ecological transition, and manufacturers face several challenges during their implementation.
Initial investment
One of the main challenges is the initial cost of implementing eco-friendly technologies and manufacturing processes. Upgrading equipment and incorporating renewable energy sources may require significant initial investment. However, it is important to consider cost savings and long-term benefits that sustainability can bring.
Limited knowledge of green manufacturing practices
Another barrier is the lack of awareness and knowledge about eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Many companies may not be aware of the available technologies and strategies that can help them reduce their environmental impact. Education and training programs can play a crucial role in overcoming this barrier and empowering companies to adopt sustainable practices.
Resistance to change
Additionally, companies may face resistance from stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and customers. Resistance to change and skepticism about the benefits of green manufacturing can hinder the implementation process. Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are essential to address concerns and achieve acceptance of sustainable initiatives.
Government incentives and regulations for green manufacturing
To encourage the adoption of eco-friendly manufacturing practices, governments worldwide have implemented various policies, incentives, and regulations (Zhu et al., 2023).
A common incentive is financial support in the form of grants, tax credits, or subsidies. Governments provide financial assistance to companies investing in sustainable technologies and processes. These incentives help offset initial costs and encourage more companies to adopt green manufacturing.
Regulations are another important tool governments use to drive sustainability in the manufacturing industry. Environmental regulations set standards for emissions, waste management, and resource use, ensuring that companies comply with sustainable practices. By enforcing these regulations, governments promote a level playing field and encourage companies to prioritize sustainability.
Companies need to stay informed about incentives and regulations in their respective regions to maximize the benefits of green manufacturing and ensure compliance with environmental standards.
The Future of Sustainable Manufacturing
Due to global interest in this topic, private companies are also increasing their efforts towards environmental management (D’Angelo et al., 2023). Green manufacturing is a constantly evolving field with enormous growth potential. The development of new technologies, growing demand for sustainable products, and regulatory pressure will drive the adoption of green practices in the industry.
On the other hand, Bhatt et al. (2020) recommend integrating sustainability principles, such as sustainable development goals (SDGs), circular economy, life cycle engineering, and corporate sustainability assessment with green manufacturing research.
Additional Resources for Green Manufacturing
- Eco-Innovation Observatory: Provides information on eco-friendly innovations in different industrial sectors.
- Green Chemistry Initiative: Offers tools and resources to promote green chemistry practices in manufacturing.
- Green Electronics Council: Provides information and tools to promote the manufacturing of more sustainable electronic products.
- Circular Economy Toolbox: Provides tools and resources to help companies adopt circular economy principles in manufacturing.
- Renewable Energy World: Offers news, analysis, and resources on renewable energies that can be used in manufacturing processes.
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainability in the Manufacturing Industry
Green manufacturing is revolutionizing the industry and redefining sustainability. As companies increasingly recognize the importance of environmental responsibility, eco-friendly manufacturing practices and innovations are gaining momentum.
The benefits of adopting green manufacturing are substantial, including cost savings, better product quality, and access to a growing market of environmentally conscious consumers. However, challenges such as initial costs and resistance to change need to be overcome.
With government incentives and regulations supporting sustainability efforts, companies have the opportunity to embrace green manufacturing and contribute to a more sustainable future. By using tools and technologies to measure and monitor sustainability performance, companies can track their progress and continuously improve.
The transition to green manufacturing requires a strategic and systematic approach involving all stakeholders. By taking necessary steps and committing to sustainability, companies can play a crucial role in shaping the future of the manufacturing industry and creating a more sustainable world.
References
Afum, E., Agyabeng-Mensah, Y., Sun, Z., Frimpong, B., Kusi, L.Y. and Acquah, I.S.K. (2020), “Exploring the link between green manufacturing, operational competitiveness, firm reputation and sustainable performance dimensions: a mediated approach“, Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, Vol. 31 No. 7, pp. 1417-1438. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMTM-02-2020-0036
Al-Hakimi, M. A., Al-Swidi, A. K., Gelaidan, H. M., & Mohammed, A. (2022). The influence of green manufacturing practices on the corporate sustainable performance of SMEs under the effect of green organizational culture: A moderated mediation analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 376, 134346.
Andaregie, A., & Astatkie, T. (2022). Determinants of the adoption of green manufacturing practices by medium-and large-scale manufacturing industries in northern Ethiopia. African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development, 14(4), 960-975.
Bhatt, Y., Ghuman, K., & Dhir, A. (2020). Sustainable manufacturing. Bibliometrics and content analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 260, 120988.
D’Angelo, V., Cappa, F., & Peruffo, E. (2023). Green manufacturing for sustainable development: The positive effects of green activities, green investments, and non‐green products on economic performance. Business Strategy and the Environment, 32(4), 1900-1913.
Guo, H., & Tsinopoulos, C. (2023). Enabling a circular economy through green manufacturing in chinese apparel manufacturers: antecedents and outcomes. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management.
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Singh, R. P., Suman, R., & Qadri, M. A. (2023). A pervasive study on Green Manufacturing towards attaining sustainability. Green Technologies and Sustainability, 100018.
Kannan, D., Shankar, K. M., & Gholipour, P. (2022). Paving the way for a green transition through mitigation of green manufacturing challenges: A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 368, 132578.
Saxena, Ankur and Srivastava, Ankita, Industry Application of Green Manufacturing: A Critical Review (February 25, 2022). Journal of Sustainability and Environmental Management, Vol. 1, No. 1 (2022), 32 – 45, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4043769
Yan, Z., Shi, R., Du, K., & Yi, L. (2022). The role of green production process innovation in green manufacturing: Empirical evidence from OECD countries. Applied Economics, 54(59), 6755-6767.
Zhu, J., Lu, Y., Song, Z., Shao, X., & Yue, X. G. (2023). The choice of green manufacturing modes under carbon tax and carbon quota. Journal of Cleaner Production, 384, 135336.
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.