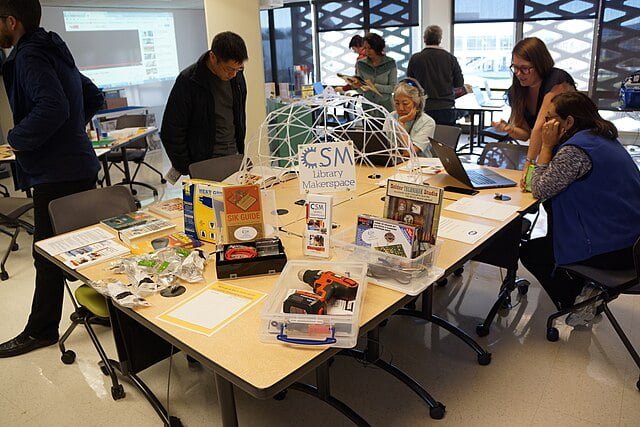
In a world where innovation and originality reign, the concept of makerspaces has become a powerful catalyst for creativity. Makerspaces are workshops or collaborative spaces equipped with cutting-edge tools and technology, aimed at inspiring people to turn their ideas into tangible realities.
By providing a stimulating and supportive environment, makerspaces enable individuals to explore their passions, experiment with different materials, and develop technical skills. From 3D printers and laser cutters to coding and robotics, these spaces offer a wide range of resources to fuel imagination and innovation.
Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur, a curious hobbyist, or an experienced professional, the potential of collaborative spaces knows no bounds. Not only do they foster skill development, but they also promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration — essential skills in today’s fast-paced world.
In this article, we aim to provide you with basic information about makerspaces and the impacts they are generating in the educational and entrepreneurial fields.
What is a makerspace?
Makerspaces are community-centered learning environments that provide access to tools, technologies, and materials for hands-on learning and creative exploration. They foster a culture of experimentation, collaboration, and problem-solving, allowing individuals to turn their ideas into tangible creations.
These collaborative spaces are typically equipped with a wide variety of tools and technologies that enable people to bring their ideas to life. From woodworking and electronics to computer programming and 3D printing, makerspaces offer a variety of resources to support a wide range of interests and projects.
Key features of Makerspaces
According to Albuquerque and Cavalcante (2023), there is consensus on the characteristics of makerspaces with five essential elements: physical space, equipment and materials, projects and activities, guidance and support, and assessment and feedback.
Furthermore, other key features of makerspaces include:
- Open access: Makerspaces are collaborative spaces and are often open to the public, providing a welcoming environment for people of all ages, backgrounds, and skill levels.
- Hands-on learning: Makerspaces emphasize hands-on learning and encourage participants to interact with tools, materials, and technologies to gain practical experience.
- Collaboration: Collaboration is at the core of makerspaces, as it fosters a sense of community and encourages people to share ideas, knowledge, and expertise. Smith (2017) highlights that these places are also spaces for networking to reflect and discuss about the design and crafting of society; thus creating spaces for social innovation.
- Problem-solving: Makerspaces promote problem-solving skills by providing a platform for people to tackle challenges and develop innovative solutions.
Differences between Makerspaces and FabLabs
While the terms “makerspaces” and “fablabs” are often used interchangeably, there are some subtle differences between these two concepts, as described in the following table:
| Features | Makerspaces | Fab Labs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative spaces for hands-on learning and creative exploration | Manufacturing laboratories for rapid prototyping and digital fabrication |
| Emphasis | Creativity, collaboration, problem-solving, hands-on learning | Rapid prototyping, digital design, digital fabrication |
| Target Audience | Broad | Individuals with interest in technology, engineering, and design |
| Resources | Basic tools, arts and crafts materials, computers, internet access | Digital fabrication tools, design software, access to global Fab Labs networks |
| Funding | Diverse | Often associated with educational or research institutions |
| Examples | Libraries, community centers, schools, coworking spaces | MIT Media Lab, Fab Lab Barcelona, Fab Lab Santiago |
It is worth noting that these are general distinctions and that the boundaries between makerspaces and fab labs may blur in some cases. In practice, many spaces share characteristics of both types. What’s important is that these spaces provide a conducive environment for creativity, innovation, and hands-on learning.
Benefits of Makerspaces
Makerspaces offer a multitude of benefits that go far beyond mere creation and tinkering. These innovative spaces provide fertile ground for fostering creativity, enhancing hands-on learning, promoting collaboration, boosting problem-solving, and cultivating STEM skills.
Here are some key advantages of engaging with makerspaces:
Creativity
Makerspaces provide an environment that fosters creativity and encourages people to think innovatively. By offering access to a wide range of tools and technologies, makerspaces inspire individuals to explore new ideas, experiment with different materials, and push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Skill Development
Makerspaces are excellent platforms for learning and skill development. Whether mastering a new programming language, honing woodworking techniques, or understanding circuits, makerspaces offer the resources and support needed to acquire and refine technical skills. Regarding this, Rayna and Striukova (2021) highlight that collaborative spaces allow for skills development beyond what is generally considered 21st-century digital skills because they combine digital skills with practical “making” skills, as they are themselves a mixed environment, both digital and physical.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Makerspaces promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills. When faced with a challenge or project, individuals must analyze the problem, devise a plan, and troubleshoot along the way. This process encourages people to think critically, overcome obstacles, and develop innovative solutions.
Collaboration and Community
Collaborative spaces foster collaboration and community building. By bringing together people from diverse backgrounds and experiences, makerspaces create opportunities for individuals to learn from one another, share knowledge, and work together on projects. Regarding this, Holm (2015) indicates that the maker movement generates dense but diverse networks, creating new ideas and innovative thinking; likewise, Diaz et al. (2021) report that, analyzing the case of the public network of makerspaces in Barcelona: the Ateneus de Fabricació and in the context of smart cities, the free access to public makerspaces is accompanied by a change in the relationship between public entities and users to promote the empowerment of the inhabitants of Barcelona.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Makerspaces democratize access to technology and, therefore, enhance possibilities for innovation and entrepreneurship (Zakoth, et al., 2014). Access to tools, technologies, and a supportive community allows individuals to create prototypes and test their ideas, turning them into viable products or services. In this way, makerspaces have become incubators for new businesses and have played a significant role in launching successful ventures. Regarding this, van Holm (2017) highlights that these spaces have four main contributions to economic development:
(a) creating a cultural shift by fostering entrepreneurship in the community,
(b) supporting the growth of small businesses by providing services,
(c) providing workforce training, and
(d) increasing workforce retention.
Cultivating STEM Skills and Interests
Makerspaces provide a gateway to STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education, offering engaging and hands-on experiences that spark interest and develop essential STEM skills. Soomro et al. (2023) identified seven methods through which collaborative spaces can foster creativity in STEM disciplines; the most important methods were multidisciplinary collaboration, carefully choosing pedagogy, and not restricting students’ imagination.
Promoting Sustainable Development
Bobic (2023) reveals that makerspaces contribute as learning spaces to sustainable development in various ways, educating participants about sustainable development but also fostering innovation, debate, and social action towards global sustainability and justice goals.
Overall, makerspaces offer a variety of benefits that go beyond the development of technical skills. They foster creativity, encourage collaboration, and empower individuals to become innovators and entrepreneurs.
Makerspaces in Education
Makerspaces have become increasingly popular in educational settings, from elementary schools to universities. These spaces provide students with hands-on learning experiences and opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in practical ways; thus, makerspaces can be understood as spaces that generate new dynamics of collaborative learning (Oliver-Espinoza, 2021).
Regarding this, Soomro et al. (2023) report that makerspaces are gaining popularity in educational activities across all age groups, from elementary schools to higher education institutions, particularly in the STEM disciplines.
In makerspaces, students can engage in project-based learning, where they tackle real-world problems and develop tangible solutions. This approach not only enhances students’ understanding of core subjects but also cultivates essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and teamwork.
Makerspaces also promote interdisciplinary learning by integrating various subjects and encouraging students to explore connections between different fields. For example, a project involving robotics may require students to learn concepts from computer science, engineering, and physics, fostering a holistic understanding of these disciplines.
Additionally, makerspaces provide a platform for students to develop their creativity and entrepreneurial skills. They can brainstorm ideas, design prototypes, and present their projects to peers and mentors. This process allows students to gain confidence, develop communication skills, and learn from both successes and failures.
By incorporating collaborative spaces into educational institutions, educators are equipping students with the skills and mindset needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving job market. Makerspaces foster a sense of curiosity, ingenuity, and adaptability, qualities highly valued in today’s innovation-driven world.
Makerspaces in Libraries
Libraries have long been known as repositories of knowledge and information. However, with the rise of digital resources and online access, libraries have had to reposition themselves as dynamic community spaces that offer more than just books, representing a paradigm shift, libraries are no longer built for shelves, but are spaces for creative and collaborative learning designed for innovation and knowledge creation in the digital age (Wang et al., 2016).
On the other hand, Becerra-Castillo et al. (2023) highlight that the different applications that can be provided to the makerspace within the public library can be grouped into three main areas: participatory community, technology, and learning.
In this sense, Makerspaces in libraries provide a unique opportunity for users to explore their creativity and learn new skills. These spaces offer access to a wide range of tools and technologies, such as 3D printers, sewing machines, and electronics kits. By providing these resources, libraries enable people to engage in hands-on learning experiences and transform their ideas into reality.
Makerspaces in libraries also promote community engagement and collaboration. They serve as gathering places where people can come together to share knowledge, learn from each other, and work on projects. Libraries often organize workshops, classes, and events to facilitate learning and community building within the maker space.
Additionally, makerspaces in libraries are inclusive and accessible to all. They provide a safe and supportive environment where people can experiment, make mistakes, and learn from them. By offering free or low-cost access to tools and technologies, libraries ensure that everyone has the opportunity to participate in creative making.

Makerspaces in Community Centers
Community centers play a vital role in bringing people together and fostering a sense of belonging. Makerspaces within community centers expand on this function by providing a space for individuals to explore their interests, collaborate with others, and contribute to their community.
Makerspaces in community centers offer opportunities for skill development and learning. They provide access to tools and technologies that may not be readily available to individuals, allowing them to learn new skills and develop their talents. From woodworking and metalworking to digital fabrication and coding, makerspaces offer a wide range of resources to cater to different interests and passions.
In addition to skill development, makerspaces in community centers promote social interaction and community engagement. These spaces bring together people from diverse backgrounds, creating opportunities to share knowledge, collaborate, and network. Individuals can work together on projects, learn from each other, and contribute to the betterment of their community.
Makerspaces in community centers also play a role in empowering individuals and fostering a sense of agency. By providing access to tools and resources, makerspaces give people the means to bring their ideas to life and make a positive impact. Whether it’s developing a community garden, creating artwork, or building a sustainable energy solution, makerspaces provide a platform for individuals to contribute to their community in meaningful ways.
Makerspaces in community centers are not just spaces for creating; they are spaces for community building, skill development, and empowerment. They embody the spirit of collaboration and creativity, bringing people together and inspiring positive change.
Are Makerspaces Profitable?
While makerspaces are often associated with nonprofit organizations and educational institutions, they can also be profitable businesses. By diversifying revenue streams, attracting grants and sponsorships, offering workshops and classes, partnering with businesses, and leveraging technology, makerspaces can achieve financial sustainability and expand their impact.
Some strategies to ensure the profitability of collaborative spaces include:
- Makerspaces can generate income through a variety of channels, such as membership fees, equipment and space rental fees, sales of materials and products, and organization of events and workshops.
- Makerspaces can seek funding from government grants, private foundations, and corporate sponsorships to support their programs, equipment, and facilities.
- Collaborative spaces can offer workshops and classes on a variety of topics, such as 3D printing, electronics, woodworking, and robotics, generating income and providing valuable learning opportunities for the community.
- Makerspaces can partner with local businesses and organizations to offer collaborative projects, workshops, and events, gaining exposure and potential funding opportunities.
How to Establish a Makerspace
Setting up a makerspace requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key steps to help you get started:
- Define your goals: Determine the purpose and objectives of your makerspace. Is it targeting a specific audience, such as students or entrepreneurs? What skills and knowledge do you want to promote? Clarifying your goals will help guide your decision-making process.
- Secure a space: Find a suitable location for your makerspace. Consider factors such as accessibility, size, teamwork, and availability of utilities. Depending on your budget and resources, you may need to start small and gradually expand as your maker space grows.
- Equip your space: Identify the tools and equipment you need based on your goals and target audience. Common tools found in maker spaces include 3D printers, laser cutters, soldering stations, woodworking tools, and electronics kits. Consider space and budget constraints when selecting equipment.
- Create a supportive environment: Design your space to foster creativity, collaboration, and learning. Consider design options, lighting, and storage. Provide comfortable work areas and ensure that tools and materials are easily accessible. Incorporate areas for brainstorming, prototyping, and idea sharing.
- Build a community: A makerspace is more than just tools and equipment; it’s the people who come together to create and collaborate. Foster a sense of community by organizing workshops, classes, and events. Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration among members.
- Establish safety guidelines and protocols: Develop clear safety guidelines and protocols to ensure safe and responsible use of tools and equipment. Train users on proper use and maintenance. Provide appropriate safety equipment and signage to minimize risks.
- Promote and market your makerspace: Raise awareness of your maker space through various channels. Use social media, community bulletin boards, and local events to promote your space. Collaborate with schools, libraries, and businesses to expand your reach.
Remember, establishing a makerspace is an ongoing process. Continuously evaluate and adapt your space based on the needs and feedback of your community. With careful planning and a supportive community, your makerspace can become a thriving hub of creativity and innovation.
Tools and Equipment for Makerspaces
Makerspaces are equipped with a wide range of tools and equipment that enable people to bring their ideas to life. Below are some common tools found in makerspaces:
- 3D Printers: 3D printers allow users to create three-dimensional objects by layering materials such as plastic or metal. They are widely used in various fields, including product design, engineering, and prototyping.
- Laser Cutters and Engravers: Laser cutters and engravers use a high-powered laser to cut or engrave materials such as wood, acrylic, or metal. They are popular for creating intricate designs and precise cuts.
- Soldering Stations: Soldering stations are used to join electronic components through soldering. They are essential for electronics projects and circuit board assembly.
- Woodworking Tools: Woodworking tools, such as saws, drills, and sanders, are used to shape and manipulate wood. They are essential for projects involving furniture, cabinetry, or sculpture.
- Electronics Kits: Electronics kits provide a variety of components and circuits for people to experiment with and learn about electronics. They are often used for educational purposes and prototyping electronic devices.
- Sewing Machines: Sewing machines allow people to create or modify fabric-based projects. They are commonly used for fashion design, textile art, and upholstery.
- Coding and Robotics Kits: Coding and robotics kits provide tools and resources for people to learn programming and build robots. They are popular for STEM education and developing computational thinking skills.
- Hand Tools: Hand tools, such as screwdrivers, wrenches, and pliers, are essential for various projects that require manual dexterity and precision. They are commonly used for repairing, assembling, or modifying objects.
- Digital Fabrication Tools: Digital fabrication tools, such as CNC machines and vinyl cutters, automate the process of cutting, engraving, or modeling materials based on digital designs. They are versatile tools for creating precise and complex objects.
- Computer Workstations: Computer workstations equipped with design software, programming tools, and internet access are essential for planning, designing, and researching projects. They provide the digital infrastructure for makerspaces.
The tools and equipment in makerspaces may vary depending on the specific focus and available resources. It is important to maintain and periodically update the tools to ensure their proper functioning and safety.
Makerspace Projects and Activities
Makerspaces offer a wide range of projects and activities that cater to different interests and skill levels. Below are some examples of projects commonly undertaken in makerspaces:
- Prototyping and Product Design: Makerspaces provide resources and tools for people to prototype and refine their product ideas. Whether creating a new device or designing a functional prototype, makerspaces enable people to bring their concepts to life.
- Art and Sculpture: Makerspaces are excellent spaces for artists to explore new mediums and techniques. From traditional sculpture to digital art, makerspaces offer the tools and guidance needed to create unique and innovative artwork.
- Robotics and Automation: Makerspaces provide a platform for people to learn about robotics and automation. From building simple robots to programming complex systems, maker spaces offer the resources and expertise to explore the world of robotics.
- Textile and Fashion Design: Creation spaces with sewing machines and fabric-cutting tools allow people to experiment with textile and fashion design. From creating custom garments to exploring wearable technology, makerspaces provide the tools and support for textile projects.
- Environmental and Sustainable Solutions: Makerspaces are spaces for people to develop innovative solutions to environmental challenges. Whether designing a solar-powered device or creating a sustainable garden, collaborative spaces provide the resources and guidance to create positive change.
- Coding and Game Development: Makerspaces often offer coding workshops and resources for people to learn programming languages and develop their games or applications. These activities promote computational thinking and digital literacy.
- Woodworking and Carpentry: Makerspaces equipped with woodworking tools allow people to work with wood and create functional and decorative objects. From furniture making to woodworking crafts, collaborative spaces provide the tools and expertise for woodworking projects.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of projects and activities that can be undertaken in makerspaces. The possibilities are endless, limited only by imagination and creativity.
Where to Find a Makerspace?
Due to their importance, makerspaces are being implemented worldwide. Below, we offer a directory that gathers information about maker spaces located near you:
Conclusion
Makerspaces are not just places to make things; they are catalysts for creativity, innovation, and transformation. By fostering a culture of hands-on learning, collaboration, and problem-solving, maker spaces empower individuals, revitalize communities, and shape the future of learning and innovation. As we embrace the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, makerspaces will continue to play an increasingly important role in shaping a brighter, more creative, and innovative future.
Bibliographic References
ALBUQUERQUE, Cassiano Henrique de; CAVALCANTE, Patrícia Smith. Ensino e Aprendizagem através de Makerspaces: uma Revisão Sistemática da Literatura. In: ACTAS DEL SIMPOSIO BRASILEÑO SOBRE INFORMÁTICA EN EDUCACIÓN (SBIE), 34. , 2023, Passo Fundo/RS. Anais […]. Porto Alegre: Sociedade Brasileira de Computação, 2023 . p. 311-322. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5753/sbie.2023.234933.
Becerra-Castillo, S., Calderón-Durán, A., & Duarte-Venegas, G. USOS DEL MAKERSPACE EN LA BIBLIOTECA. Serie Bibliotecología y Gestión de Información, n.º 126, diciembre 2023
Bobic, O. R. (2023). Makerspaces as learning spaces for sustainable development. A systematic literature review. Revista de Științe ale Educației, 48(2), 32-45.
Diaz, J., Tomàs, M., & Lefebvre, S. (2021). Are public makerspaces a means to empowering citizens? The case of Ateneus de Fabricació in Barcelona. Telematics and Informatics, 59, 101551.
Holm, E. J. V. (2015). Makerspaces and Contributions to Entrepreneurship. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, 24-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.167
Oliver-Espinoza, R. (2021). Makerspaces: indicadores cienciométricos e implicaciones para la innovación, la educación y el emprendimiento. Entreciencias: diálogos en la sociedad del conocimiento, 9(23).
Rayna, T., & Striukova, L. (2021). Fostering skills for the 21st century: The role of Fab labs and makerspaces. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 164, 120391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120391
Smith, A. (2017). Innovación social, democracia y makerspaces. Revista española del tercer sector, 36, 49-74.
Soomro, S. A., Casakin, H., Nanjappan, V., & Georgiev, G. V. (2023). Makerspaces fostering creativity: A systematic literature review. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 32(4), 530-548.
van Holm, E. J. (2017). Makerspaces and Local Economic Development. Economic Development Quarterly, 31(2), 164-173. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242417690604
Wang, F., Wang, W., Wilson, S., & Ahmed, N. (2016). The state of library makerspaces. International Journal of Librarianship, 1(1),2-16. https://doi.org/10.23974/ijol.2016.vol1.1.12
Zakoth, D., Mauroner, O., & Emes, J. (2024). The role of makerspaces in innovation processes: An exploratory study. R&D Management, 54(2), 398-428. https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12594
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.