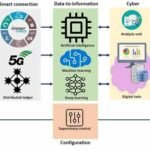
In the world of modern business, information is power. The ability to collect, analyze, and leverage data has become an invaluable asset for companies of all sizes and industries.
Business intelligence (BI) has become a significant focus to ensure the competitiveness of companies, as it enables you to gather, analyze, and leverage data generated across various platforms where you interact with your customers.
The days of using paper to record and store customer data, supplier information, or your company’s processes are now history. If you are still recording your business information in Microsoft Excel or Google Drive templates without conducting subsequent analysis, you are heading towards obsolescence.
In recent years, with the emergence of Industry 4.0, managers and decision-makers have been paying more attention to business intelligence (Ain et al., 2019) due to its capacity to provide systematic information that aids in business decision-making.
Likewise, it is highly likely that your business has an account on Facebook, Instagram, or another social network, and you only use it for occasional posts. Let me tell you that you are missing out on data and information about your current or potential customers that can be used to innovate and become more competitive.
In this article, we want to introduce you to Business Intelligence, a tool that can provide you with significant value through the collection and analysis of data generated by your company’s processes and interactions with your customers on social media.
Business Intelligence and Decision-Making
As a business owner, you continually face decision-making regarding the launch of a new product, promotions and offers, evaluating suppliers, or increasing the number of customers. This raises the question: How to make the best decisions?
The rapidly changing business environment means that companies capable of harnessing information about their customers, markets, suppliers, and operations will be able to benefit from opportunities and gain a competitive advantage (Fombellida et al., 2018).
In companies, the primary component of decision-making is information, and this information resides in databases that every company accumulates with data about their suppliers, employees, customers, and more.
Currently, companies have more information about their sales, customer preferences, and suppliers, but less time to analyze it. Additionally, the use of digital technologies generates a vast amount of data that is leveraged by Business Intelligence (BI) to make decisions and enhance business management (Basile et al., 2023).
In the current context, business intelligence aims to support the growth of companies and other types of organizations, improving their competitiveness by facilitating decision-making.
Business Intelligence is more than a computer program; it is an information management philosophy that transforms raw data into knowledge, enabling decision-making (Murillo and Cáceres, 2013).
Business Intelligence is a way to collect, correlate, and analyze events from multiple sources. This information can be used to enhance your products or services for your customers.
Definition of Business Intelligence (BI)
You may be wondering, “What is Business Intelligence?” Here are some of the most widely accepted definitions:
Howard Dresner, a Gartner consultant, popularized the term Business Intelligence, defining it as “an interactive process for exploring and analyzing structured information in an area (usually stored in a data warehouse) to discover trends or patterns, from which to derive ideas and draw conclusions.”
Lluís (2007) emphasizes that “through the use of technologies and Business Intelligence methodologies, we aim to turn data into information and, from that information, be able to discover knowledge.”
Murillo and Cáceres (2013) indicate that business intelligence can be understood as a set of mathematical models and analysis methodologies that consider the available data from a process or business.
Business Intelligence aims to logically investigate, integrate, and collect data from various sources of customer information, environment, competitors, markets, etc., in a multidimensional analysis to enhance business performance (Huang et al., 2022).
In essence, Business Intelligence, or BI, involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting data to assist in business decision-making. It is the process of turning data into valuable information for the company.
It is important to note that Business Intelligence is an umbrella term for strategies, technologies, and information systems used by companies to extract relevant knowledge from data, according to the value chain, to support a wide range of operational, tactical, and strategic business decisions (Muntean, 2018).
Benefits of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence has become an essential tool for entrepreneurs because it offers many benefits to companies that implement BI systems.
Huang et al. (2022) report that Business Intelligence improves the innovation capacity of companies and, consequently, the financial performance of startups.
In a world where Industry 4.0 is gaining ground, the generation of data from multiple devices can become essential inputs for the implementation of BI systems that assist in decision-making, both in processes and in interactions with customers.
Tavera et al. (2021) report that Business Intelligence has become indispensable for strategic decision-making in companies and governments worldwide. It plays a significant role in business survival, maintaining relationships with other companies, counterintelligence, goals and objectives in both the short and long term.
Companies often collect unstructured data, and in this regard, business intelligence helps gather essential information from a wide variety of unstructured data and convert it into actionable information that enables companies to make informed policy decisions and improve business efficiency and productivity (Niu et al., 2021).
The results of Daradkeh’s (2019) research showed that knowledge orientation and BI capabilities are significantly and positively related to business model innovation.
Examples and Applications of Business Intelligence
If you look at a sales receipt, you’ll notice various data points, such as date, time, items sold, item descriptions, unit price, payment method, and more.
By analyzing the data contained in sales receipts, you can access information about total sales for the day, best-selling items, payment methods, average ticket amount, operational-type information that facilitates decision-making.
Ultimately, analyzing information can help you better understand your customers, suppliers, and your company’s processes.
If you lack tools, converting data into information and then into knowledge can be a tedious process.
The applications of Business Intelligence are found in all business fields; however, Lluís (2007) highlights that business intelligence is useful for:
- Purchasing managers: to understand which items are selling the most and their sales trends.
- Sales managers: to see which products have the highest turnover.
- Negotiation managers: cash flows, credit or debit cards.
- Marketing managers: to assess the effectiveness of promotions.
- Personnel managers: shift allocation.
There are numerous examples of Business Intelligence that span various industries. Here are some concrete examples:
- Retail: A chain of retail stores can use BI to analyze historical sales and predict product demand at different locations.
- Healthcare: Hospitals can use BI to improve resource management, optimize appointment scheduling, and enhance patient care. Basile et al. (2023) studied whether a data-exploitation-based decision support system (DSS) model through BI could outperform traditional experience-based practices in managing processes in healthcare, and they concluded that the DSS model leads to a more accurate estimation of potential cost savings in the treatment of oncology patients, allowing for significant cost savings.
- Finance: Financial institutions can use BI to identify fraud patterns and make more informed investment decisions.
- Manufacturing: Factories can use BI to optimize the supply chain, reduce production costs, and improve product quality. Jafari et al. (2023) showed that BI, integration, and agility play an important role in achieving better supply chain performance.
Business Intelligence Implementation
Before embarking on the implementation of a Business Intelligence system, you should consider some important aspects to ensure that this process is successful.
Trieu (2023) highlights the influence of key complementary organizational resources (i.e., data-driven culture (DBC), data quality in source systems, and decision-making autonomy) on employees’ actual use of BI (which includes BI system dependence and BI system infusion) and their performance in decision-making.
Business Intelligence Tools or Software
Before implementing Business Intelligence tools, you need to assess your needs. It is important to note that BI tools should incorporate business research, data extraction, data visualization, data tools, infrastructure, and best practices to help companies make more data-driven decisions (Shao et al., 2022).
Within this framework, Business Intelligence requires three main categories of tools:
a) Data Storage
a.1. Data Warehouse: A corporate database designed to handle large volumes of data from various sources or types, characterized by its ability to integrate and cleanse information from one or more sources (Murillo and Cáceres, 2013).
b) Analytical Tools
c) Data Reporting or Presentation Tools
Which Tool to Choose?
To better understand how Business Intelligence works, it’s essential to know the tools that make it possible. There are numerous BI solutions available in the market, and choosing the right one for your company will depend on your specific needs.
There are many tools you can use to implement a Business Intelligence system in your organization. However, if you want a professional opinion, you can visit the website of the consulting firm Gartner, which publishes a classification of analytics and Business Intelligence tools every year.
According to Gartner’s classification for 2021, the top ten Business Intelligence tools are:
a) Microsoft Power BI
b) Qlik Sense
c) Oracle Analytics Cloud
d) Sinsense
e) IBM Cognos Analytics
f) Tableau Desktop
g) Looker
h) Microstrategy
i) ThoughtSpot
j) SAP Analytics Cloud
Digital Business Intelligence Kit
Business Intelligence has also given rise to a set of tools known as the “Digital Business Intelligence Kit.” This kit includes software, hardware, and methodologies that enable companies to implement BI solutions effectively. By using a digital BI kit, companies can accelerate their ability to make the most of their data.
Key elements of a Digital Business Intelligence Kit include:
- BI Software: Software platforms that enable report creation, data analysis, and visualization.
- Optimized Hardware: Servers and storage systems designed to handle large volumes of data and analytics efficiently.
- Methodologies and Best Practices: Proven approaches for the successful implementation of BI solutions within an organization.
Where to Learn Business Intelligence?
Below, we provide you with a list of courses that are available online, with the majority of them offering free content to help you acquire basic knowledge in BI. Please note that some of them also offer paid options to obtain certificates or access premium content.
- Microsoft Power BI – Free Course
- Platform: Microsoft Learn
- Description: Learn how to use Microsoft Power BI to create data visualizations and interactive dashboards.
- Link: Microsoft Power BI – Free Course
- Coursera: Business Intelligence Concepts, Tools, and Applications
- Platform: Coursera (Audit option available)
- Description: Offered by the University of Colorado, this course introduces you to BI concepts and tools.
- Link: Business Intelligence Concepts, Tools, and Applications
- edX: Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing
- Platform: edX (Audit option available)
- Description: Taught by the University of Colorado, this course covers the fundamentals of BI and data warehousing.
- Link: Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing
- IBM Cognos Analytics – Free Course
- Platform: IBM Developer
- Description: Learn how to use IBM Cognos Analytics to create reports and dashboards.
- Link: IBM Cognos Analytics – Free Course
- Tableau Training Videos
- Platform: Tableau
- Description: Tableau offers a series of free training videos covering various aspects of their BI software.
- Link: Tableau Training Videos
- Google Data Studio – Free Course
- Platform: Google Analytics Academy
- Description: Learn how to use Google Data Studio to create data reports and visualizations.
- Link: Google Data Studio – Free Course
- SQL Courses on Codecademy
- Platform: Codecademy (Free portion available)
- Description: Learn SQL, an essential language for data extraction and manipulation in BI.
- Link: SQL Courses on Codecademy
- Free MicroStrategy Courses
- Platform: MicroStrategy Education
- Description: MicroStrategy offers a variety of free courses on their BI platform.
- Link: MicroStrategy Education
- QlikView – Free Introduction Course
- Platform: Qlik
- Description: Learn the basics of QlikView, a BI tool.
- Link: Free Introduction to QlikView Course
- Power Query and Power Pivot for Excel – Free Course
- Platform: ExcelJet
- Description: Learn how to use Power Query and Power Pivot to analyze data in Excel.
- Link: Power Query and Power Pivot for Excel – Free Course
Conclusion
In summary, Business Intelligence is a powerful tool for modern businesses. It enables the collection and analysis of data to make informed and strategic decisions. We have explored what Business Intelligence is, its tools, examples, and its relationship with artificial intelligence.
As businesses continue to evolve in the digital age, BI will become an even more critical asset. In this regard, if you are a business owner, you should start developing competencies in the use of business intelligence tools to analyze the data generated in your organization, with the aim of innovating and staying competitive.
In this context, Wee et al. (2023) recommend that it is necessary to develop various business intelligence leadership skills to promote the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises. Researchers suggest that SME leaders should learn about data management, analytical skills, business processes, social and cultural changes, and investment decisions to achieve sustainable operational, management, and strategic goals.
Business Intelligence is an information management philosophy that should become a significant tool for current and future businesses. However, it should be integrated with other tools such as ERP and the Internet of Things to implement Industry 4.0.
References
Ain, N., Vaia, G., DeLone, W. H., & Waheed, M. (2019). Two decades of research on business intelligence system adoption, utilization and success–A systematic literature review. Decision Support Systems, 125, 113113.
Basile, L. J., Carbonara, N., Pellegrino, R., & Panniello, U. (2023). Business intelligence in the healthcare industry: The utilization of a data-driven approach to support clinical decision making. Technovation, 120, 102482.
Daradkeh, M. The Nexus between Business Analytics Capabilities and Knowledge Orientation in Driving Business Model Innovation: The Moderating Role of Industry Type. Informatics 2023, 10, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10010019
Fombellida, J., Martín-Rubio, I., Torres-Alegre, S. et al. Tackling business intelligence with bioinspired deep learning. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 13195–13202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3377-5
Huang, SC., McIntosh, S., Sobolevsky, S. et al. Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence in Industry. Inf Syst Front 19, 1229–1232 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9804-9
Huang, Z. X., Savita, K. S., & Zhong-jie, J. (2022). The Business Intelligence impact on the financial performance of start-ups. Information Processing & Management, 59(1), 102761.
Jafari, T., Zarei, A., Azar, A. and Moghaddam, A. (2023), “The impact of business intelligence on supply chain performance with emphasis on integration and agility–a mixed research approach“, International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, Vol. 72 No. 5, pp. 1445-1478. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-09-2021-0511
Lluís J. 2007. Business Intelligence: Competir con Información. Banesto Fundación Cultural, Escuela Banespyme, ESADE. 393 p.
Muntean M. 2018. Business Intelligence Issues for Sustainability Projects. Sustainability 2018, 10, 335; doi:10.3390/su10020335
Murillo Junco, Mary Julieth; Cáceres Castellanos, Gustavo. Business intelligence y la toma de decisiones financieras: una aproximación teórica. Revista Logos, Ciencia & Tecnología, vol. 5, núm. 1, julio-diciembre, 2013, pp. 119-138.
Niu, Y., Ying, L., Yang, J., Bao, M., & Sivaparthipan, C. B. (2021). Organizational business intelligence and decision making using big data analytics. Information Processing & Management, 58(6), 102725.
Shao, C., Yang, Y., Juneja, S., & GSeetharam, T. (2022). IoT data visualization for business intelligence in corporate finance. Information Processing & Management, 59(1), 102736.
Subba C., R. Sankar and B. Srinivasa. 2019. A Survey on Business Intelligence Tools for Marketing, Financial, and Transportation Services. S. C. Satapathy et al. (eds.), Smart Intelligent Computing and Applications, Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies 105, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1927-3_53
Tavera Romero, C.A.; Ortiz, J.H.; Khalaf, O.I.; Ríos Prado, A. Business Intelligence: Business Evolution after Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10026. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810026
Trieu, V.-H. (2023), “Towards an understanding of actual business intelligence technology use: an individual user perspective“, Information Technology & People, Vol. 36 No. 1, pp. 409-432. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-11-2020-0786
Wee, M., Scheepers, H. and Tian, X. (2023), “The role of leadership skills in the adoption of business intelligence and analytics by SMEs“, Information Technology & People, Vol. 36 No. 4, pp. 1439-1458. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-09-2021-0669
Editor and founder of “Innovar o Morir” (‘Innovate or Die’). Milthon holds a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation (UPV) and Market-Oriented Innovation Management (UPCH-Universitat Leipzig). He has practical experience in innovation management, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA) and worked as a consultant on open innovation diagnostics and technology watch. He firmly believes in the power of innovation and creativity as drivers of change and development.